Understanding the Credit Utilization Ratio: A Key Factor in Your UK Credit Score
Your credit utilization ratio is a crucial element in determining your credit score, and it plays a significant role in how lenders assess your financial responsibility. In the United Kingdom, this ratio is calculated as the percentage of your total available credit that you are currently using. This metric is one of the most influential factors in your credit score, alongside payment history.
What Is Credit Utilization Ratio?
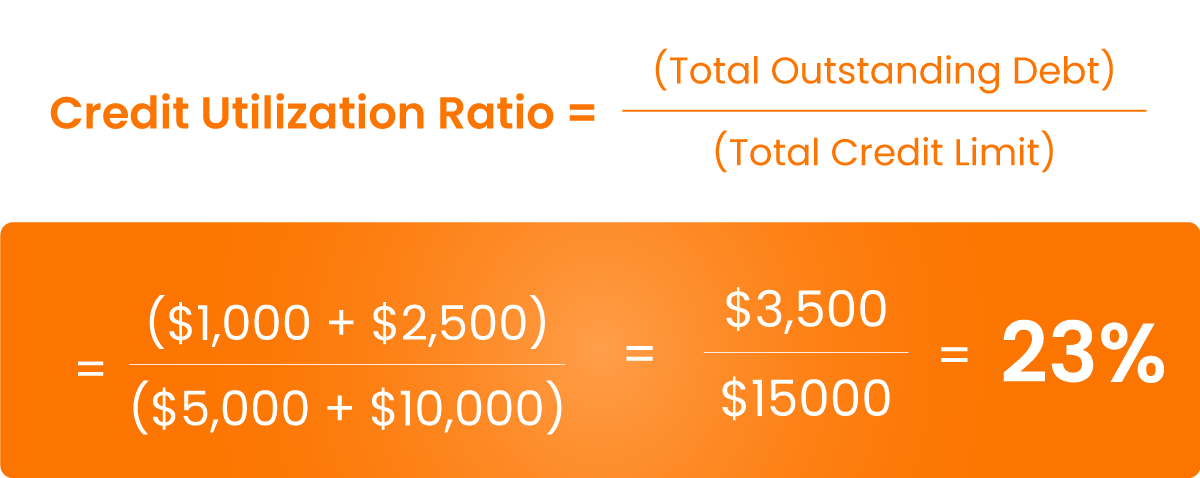
The credit utilization ratio refers to the amount of revolving credit you’re using compared to the total credit available to you. Revolving credit includes credit cards, store cards, and other similar accounts where you can borrow up to a set limit and repay it over time. The ratio is typically expressed as a percentage and is a key factor in calculating your credit score.
Maintaining a low credit utilization ratio is essential for a healthy credit score. Lenders prefer borrowers who use less than 30% of their available credit. This demonstrates responsible credit management and reduces the risk of default.
How to Calculate Your Credit Utilization Ratio

To calculate your credit utilization ratio, follow these steps:
- Add up all your outstanding balances on all your credit accounts.
- Add up the credit limits on all your credit accounts.
- Divide your total balances by your total credit limit.
- Multiply the result by 100 to get the percentage.
For example, if you have three credit cards with balances of £1,000, £2,500, and £4,000, and credit limits of £5,000, £10,000, and £8,000 respectively, your total balance is £7,500, and your total credit limit is £23,000. Your credit utilization ratio would be approximately 32.6%.
The Impact of Credit Utilization on Your Credit Score

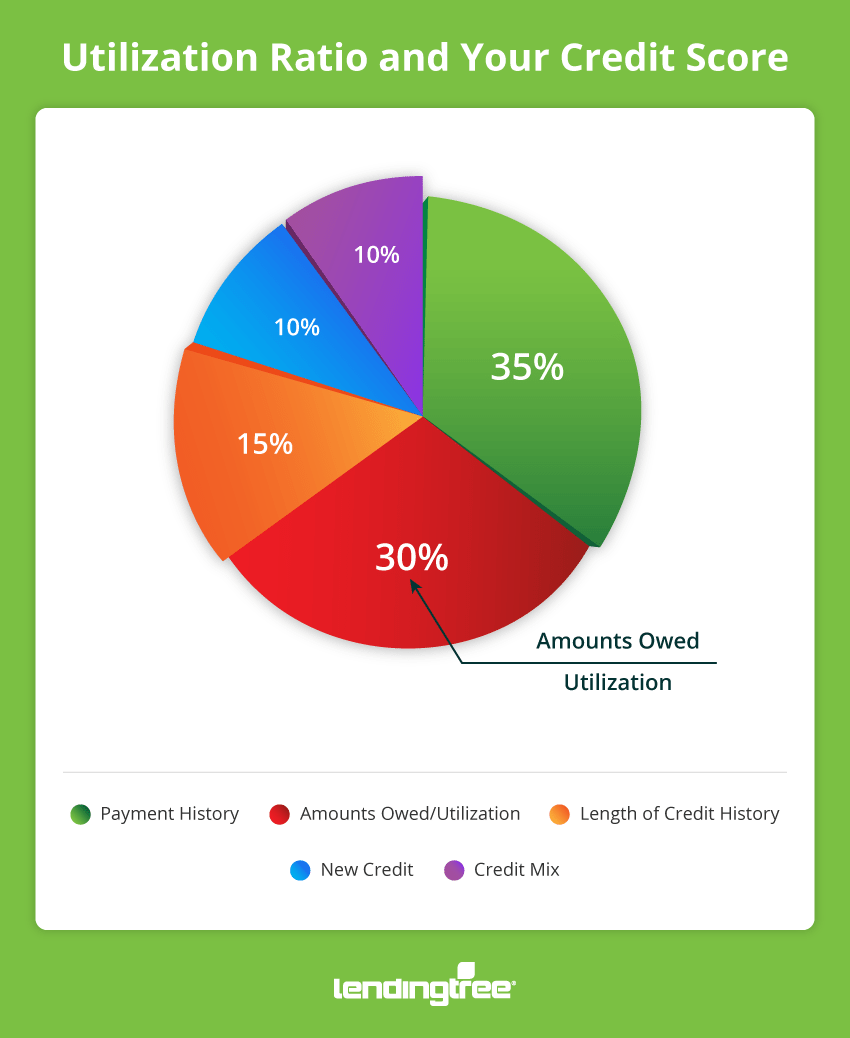
Credit utilization significantly affects your credit score, as it accounts for 30% of your overall score. High utilization can signal financial instability, while a low ratio shows you manage your credit responsibly.
Lenders consider your credit utilization when deciding whether to approve a loan or credit card application. A high ratio may lead to higher interest rates or even rejection. Conversely, maintaining a low ratio can improve your chances of securing favorable terms.
Strategies to Improve Your Credit Utilization Ratio

Here are some effective strategies to lower your credit utilization ratio:
- Pay down your debt: Reducing your outstanding balances directly lowers your utilization ratio.
- Request a credit limit increase: Increasing your credit limit can help lower your ratio without reducing your spending.
- Avoid closing unused credit accounts: Closing accounts reduces your total available credit, which can increase your utilization ratio.
- Make payments throughout the month: Paying off part of your balance regularly can lower the reported balance, improving your ratio.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Certain actions can negatively impact your credit utilization ratio:
- Closing unused credit accounts: This reduces your total available credit, potentially increasing your utilization ratio.
- Maxing out your credit cards: Using all your available credit can severely damage your credit score.
- Opening multiple new accounts: Each new account may trigger a hard inquiry, which can temporarily lower your score.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing your credit utilization ratio is vital for maintaining a strong credit score in the UK. By keeping your utilization below 30%, you demonstrate financial responsibility and improve your chances of securing loans and credit at favorable rates. Regularly monitoring your credit report and taking proactive steps to reduce your debt can significantly enhance your financial health.








