Understanding Cloud Scalability: The Key to Flexible and Cost-Effective IT Infrastructure
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, cloud scalability has emerged as a critical factor for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure. As organizations grow and adapt to changing market demands, the ability to dynamically adjust computing resources becomes essential. This article explores the concept of cloud scalability, its different types, and the numerous benefits it offers to modern enterprises.
What Is Cloud Scalability?
Cloud scalability refers to the capability of a cloud computing environment to expand or shrink its resources—such as storage, processing power, and bandwidth—in response to fluctuating demand. Unlike traditional on-premise systems, which require significant time and investment to scale, cloud scalability allows businesses to quickly allocate or remove resources without the need for physical hardware upgrades.
This flexibility ensures that organizations can efficiently manage their IT needs, whether they are experiencing a sudden surge in traffic or a temporary drop in workload. By leveraging cloud scalability, companies can avoid overprovisioning, reduce costs, and maintain high performance levels even during peak usage periods.
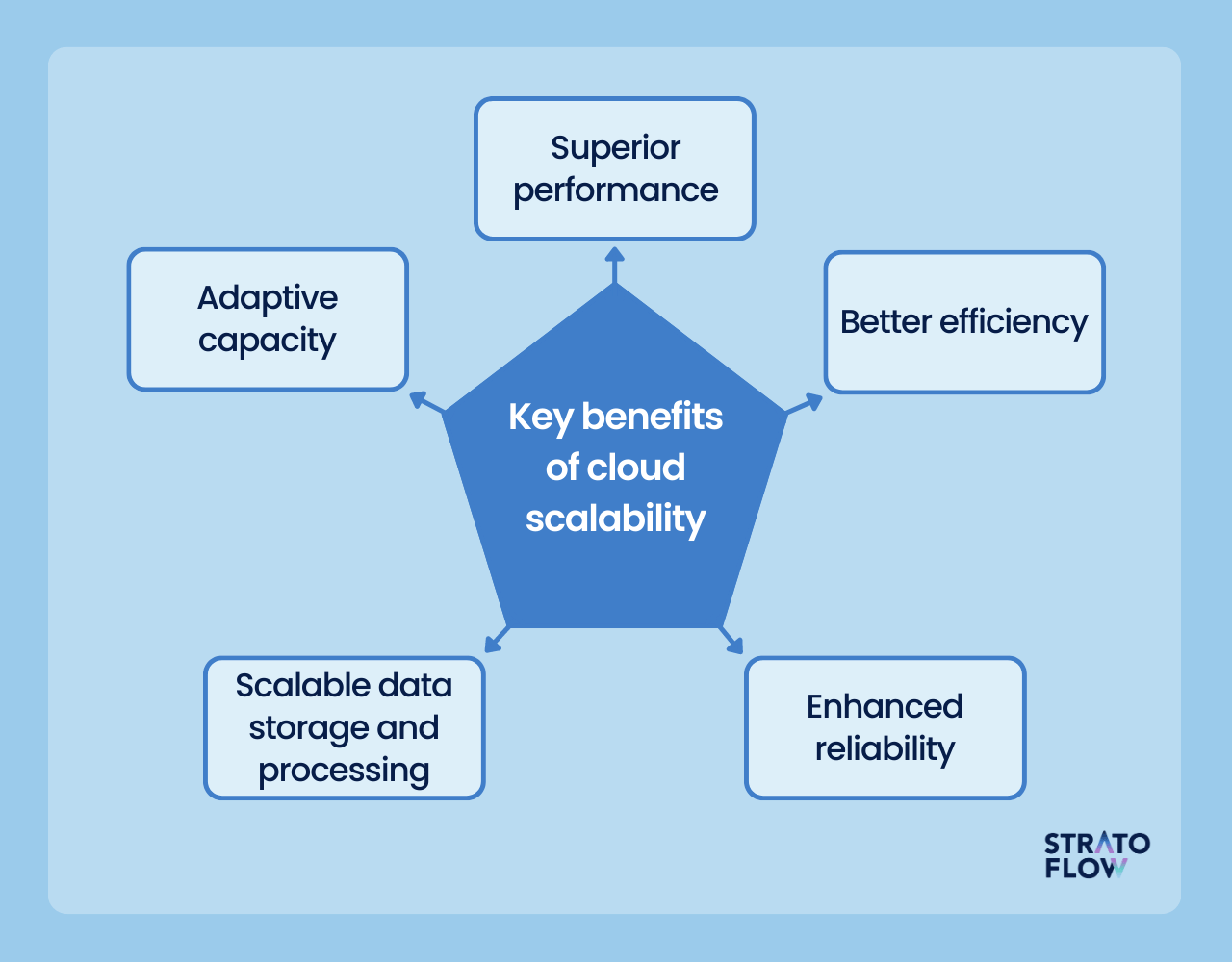
Key Benefits of Cloud Scalability
-
Cost Savings: One of the most significant advantages of cloud scalability is cost efficiency. Organizations only pay for the resources they use, eliminating the need for expensive hardware investments. This pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale up or down based on real-time demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
-
Improved Flexibility: Cloud scalability provides the flexibility needed to adapt to changing business requirements. Whether a company is expanding its operations or adjusting to seasonal fluctuations, scalable cloud solutions can easily accommodate these shifts.
-
Enhanced Performance: By automatically adjusting resources to meet demand, cloud scalability helps maintain consistent performance levels. This is particularly important for applications that require high availability and reliability, such as e-commerce platforms or online services.
-
Increased Reliability: Scalable cloud environments are designed to handle unexpected surges in traffic or workload. This ensures that businesses can continue operating smoothly without experiencing downtime or performance degradation.
-
Simplified Management: With cloud scalability, IT administrators can easily manage resources through intuitive dashboards and automation tools. This reduces the complexity of managing large-scale infrastructures and allows teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance tasks.
Types of Cloud Scalability

There are three primary types of cloud scalability, each offering unique advantages depending on an organization’s specific needs:
1. Horizontal Scalability (Scale-Out)
Horizontal scalability involves adding more instances of the same resource to a cloud environment. For example, if a web application experiences increased traffic, additional servers can be added to distribute the workload across multiple nodes. This approach is ideal for handling large-scale traffic spikes and ensuring high availability.
One of the key benefits of horizontal scalability is its ability to provide infinite growth potential. Since new instances can be added without limitations, organizations can scale their infrastructure as needed without worrying about reaching capacity constraints.
2. Vertical Scalability (Scale-Up)

Vertical scalability refers to the process of increasing the resources of an existing instance, such as adding more CPU, RAM, or storage to a single server. This method is often used for applications that require higher processing power but do not need additional instances.
While vertical scalability can improve performance, it has limitations. Servers have physical limits on how much they can be upgraded, and scaling beyond these limits may require migrating to a more powerful instance. However, this approach is still valuable for applications with predictable workloads.
3. Hybrid Scalability (Diagonal Scaling)
Hybrid scalability combines both horizontal and vertical approaches, allowing organizations to scale resources in multiple ways. This method is particularly useful for complex applications that require a combination of processing power, storage, and bandwidth.
By using hybrid scalability, businesses can optimize their infrastructure to meet varying demands. For example, they can add more servers to handle increased traffic while also upgrading individual servers to improve performance. This flexible approach ensures that organizations can adapt to changing conditions without overprovisioning or underutilizing resources.
Cloud Scalability vs. Cloud Elasticity

While cloud scalability and elasticity are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes. Cloud scalability refers to the ability of a system to grow or shrink in response to long-term demand. It involves planning and architectural decisions to ensure that the infrastructure can support future growth.
On the other hand, cloud elasticity focuses on the real-time adjustment of resources in response to short-term workload changes. It enables automatic scaling up during peak times and scaling down when demand decreases. This makes elasticity ideal for applications with fluctuating usage patterns, such as web applications or batch processing jobs.
Understanding the difference between scalability and elasticity is crucial for designing an efficient cloud infrastructure. A well-architected system should be both scalable and elastic to handle both long-term growth and short-term fluctuations.
Why Cloud Scalability Matters for Businesses

In today’s competitive landscape, businesses must be agile and adaptable to stay ahead. Cloud scalability plays a vital role in enabling this agility by providing the flexibility needed to respond to changing market conditions. Here are some reasons why cloud scalability is essential for modern organizations:
1. Supporting Business Growth
As businesses grow, their IT needs evolve. Cloud scalability ensures that organizations can easily expand their infrastructure to accommodate new users, applications, and data. This allows them to focus on innovation and customer satisfaction rather than infrastructure management.
2. Reducing Downtime
Scalable cloud environments are designed to handle unexpected traffic spikes and workload changes. This minimizes the risk of downtime and ensures that applications remain available to users at all times.
3. Enhancing User Experience
By maintaining consistent performance and availability, cloud scalability helps deliver a seamless user experience. This is especially important for applications that rely on real-time interactions, such as e-commerce platforms or online services.
4. Improving Operational Efficiency
Cloud scalability simplifies resource management by allowing businesses to automate scaling processes. This reduces the need for manual interventions and improves overall operational efficiency.
Strategies for Achieving Cloud Scalability
To fully leverage the benefits of cloud scalability, organizations should implement the following strategies:
1. Auto-Scaling
Auto-scaling is an automated process that adjusts resources based on predefined thresholds. This ensures that applications can handle increased traffic without manual intervention. Most cloud service providers offer auto-scaling features that can be configured to meet specific business needs.
2. Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, improving application performance and reliability. This technique helps prevent any single server from becoming a bottleneck and ensures that resources are used efficiently.
3. Containerization
Containerization allows applications to be packaged into lightweight, portable units that can be easily deployed and scaled. This approach simplifies resource management and enables organizations to scale their infrastructure quickly.
4. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) involves using code to manage and provision cloud infrastructure. This approach enables organizations to replicate environments and scale resources efficiently, reducing the complexity of managing large-scale infrastructures.
Conclusion
Cloud scalability is a fundamental aspect of modern IT infrastructure, offering businesses the flexibility, cost savings, and performance improvements needed to thrive in a dynamic market. By understanding the different types of scalability and implementing effective strategies, organizations can build resilient and efficient cloud environments that support their growth and innovation.
Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, embracing cloud scalability is essential for staying competitive in today’s digital landscape. With the right tools and practices, businesses can harness the full potential of the cloud and drive sustainable success.








