
The Growing Importance of Cyber Insurance in the United States
In an era where digital threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, cyber insurance has emerged as a critical tool for businesses to protect themselves from the financial and reputational damage caused by cyberattacks. As the landscape of information technology continues to evolve, so too does the need for robust insurance solutions that address the unique risks associated with digital infrastructure. This article explores the significance of cyber insurance, its historical development, current challenges, and the future of this rapidly growing sector.
Understanding Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance is a specialized form of insurance designed to help businesses manage the financial consequences of cyber incidents. These incidents can range from data breaches and ransomware attacks to business interruption caused by cyber threats. Unlike traditional insurance products, which often cover physical assets or natural disasters, cyber insurance focuses on the vulnerabilities inherent in digital systems.
The primary goal of cyber insurance is to mitigate the impact of cyberattacks by providing financial support for recovery efforts. This includes costs related to data restoration, legal liabilities, customer notifications, and even public relations management. For many businesses, especially those handling sensitive data, cyber insurance is not just a precaution—it’s a necessity.
Key Advantages of Cyber Insurance
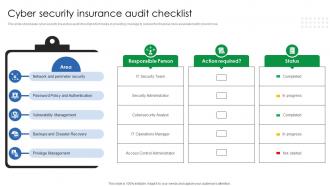
One of the most significant benefits of cyber insurance is its ability to provide a structured response to large-scale security breaches. When a company experiences a major cyber incident, the financial burden can be overwhelming. Cyber insurance offers a streamlined funding mechanism to help businesses recover and return to normal operations more quickly. This not only reduces the need for government assistance but also helps maintain business continuity.
Additionally, many cyber-insurance policies require companies to undergo IT security audits before coverage is issued. These audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that businesses are taking appropriate steps to strengthen their cybersecurity posture. In some cases, companies may be required to implement specific security measures before they can obtain coverage, further reducing the risk of future attacks.
Another advantage of cyber insurance is its role in distributing risk fairly among policyholders. Premiums are typically set based on the expected cost of potential losses, ensuring that the financial burden is shared across the industry. This approach prevents dangerous concentrations of risk and discourages free-riding, where businesses might otherwise neglect cybersecurity due to a lack of incentives.
Historical Development of Cyber Insurance

The concept of cyber insurance dates back to the late 1990s, when the first known cyber insurance product was introduced at a conference organized by the International Risk Insurance Management Society. Steven Haase, a pioneer in the field, launched the Internet Security Liability (ISL) policy in 1997, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of cyber insurance. This policy was specifically designed to address the risks associated with internet commerce.
Following this breakthrough, other companies began entering the market. In 1999, David Walsh founded CFC Underwriting in the UK, while Chris Cotterell established Safeonline around the same time. These early players laid the foundation for what would become a multi-billion-dollar industry.
Current Challenges and Rising Costs

Despite its benefits, cyber insurance is facing several challenges, particularly in terms of rising costs. According to Marsh McLennan, cyber insurance prices increased by 110% in the first quarter of 2022. This surge in premiums is largely attributed to the increasing frequency and severity of cyberattacks, particularly ransomware incidents. Insurers are struggling to accurately assess risk due to limited historical data, leading to unstable pricing models.
Moreover, the rise in cyber insurance adoption has inadvertently encouraged more ransomware attacks. Hackers are now targeting businesses that have cyber insurance, knowing that victims may be more willing to pay ransoms if they believe their insurance will cover the costs. This creates a dangerous cycle, where the availability of insurance can actually incentivize cybercriminals.
Legislative Developments
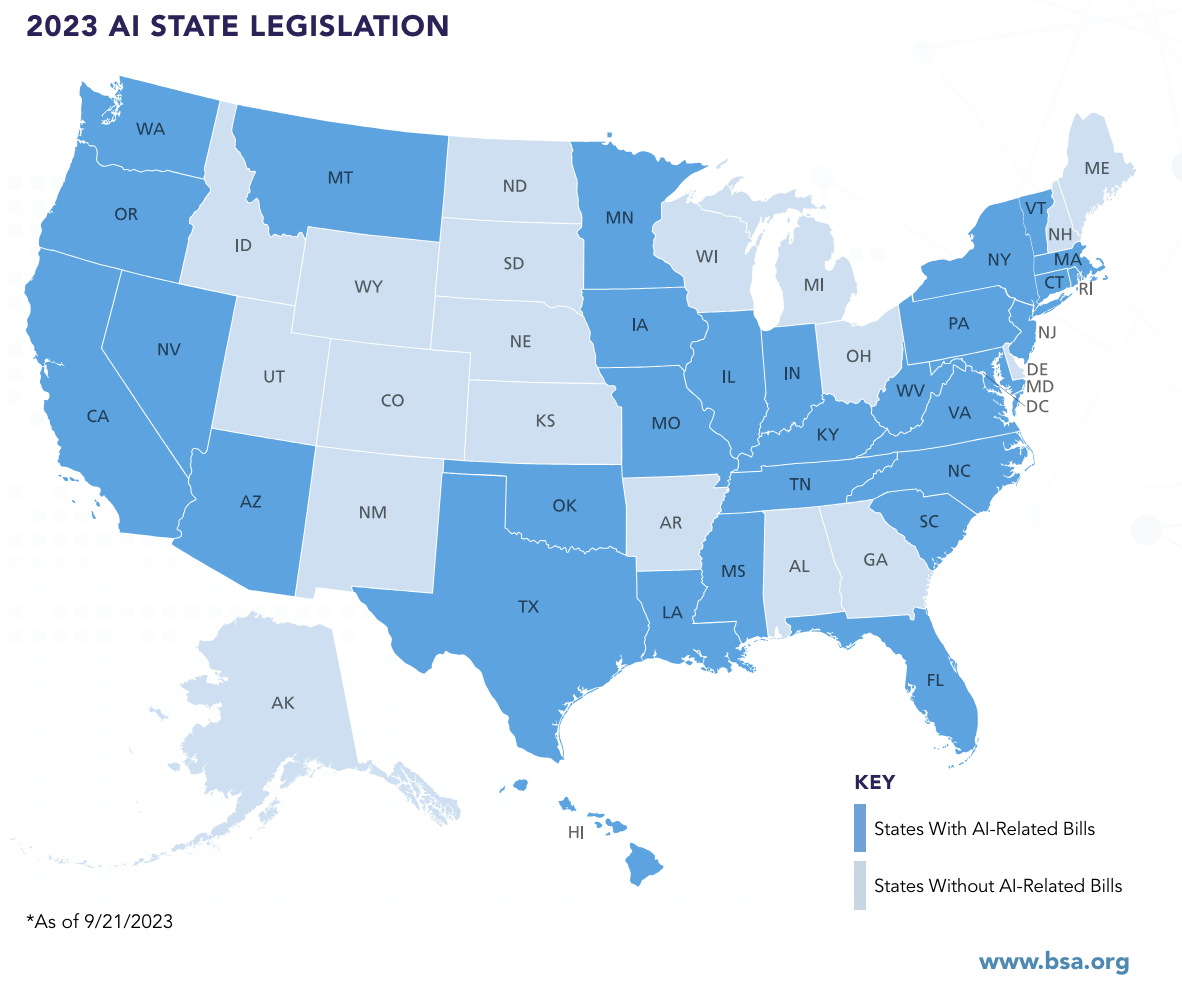
As the threat of cyberattacks continues to grow, governments are stepping in to establish regulatory frameworks. In 2022, Kentucky and Maryland enacted insurance data security legislation based on the National Association of Insurance Commissioners’ (NAIC) Insurance Data Security Model Law (MDL-668). These laws aim to enhance the cybersecurity practices of insurance companies and protect consumers from data breaches.
Maryland’s SB 207, which takes effect on October 1, 2023, and Kentucky’s House Bill 474, effective January 1, 2023, represent significant steps toward creating a more secure digital environment. These legislative efforts reflect a growing recognition of the importance of cyber insurance in safeguarding both businesses and consumers.
Future Outlook

Looking ahead, the cyber insurance market is expected to continue evolving in response to new threats and technological advancements. Insurers are increasingly focusing on risk assessment and prevention, offering consultative services to help businesses improve their cybersecurity postures. Some companies are even incorporating standards like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework into their underwriting processes.
As the demand for cyber insurance grows, so too will the need for innovative solutions to address emerging risks. From the development of cyber catastrophe (CAT) bonds to the integration of advanced data analytics, the future of cyber insurance is likely to be shaped by a combination of regulatory changes, technological innovations, and shifting market dynamics.
Conclusion
Cyber insurance has become an essential component of risk management for businesses in the United States. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for comprehensive and adaptable insurance solutions will only increase. While challenges such as rising costs and regulatory complexities remain, the long-term benefits of cyber insurance—ranging from financial protection to enhanced security practices—underscore its importance in today’s digital economy.
For businesses of all sizes, investing in cyber insurance is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a strategic decision that can help safeguard their operations, reputation, and future growth. As the landscape of cyber risk continues to shift, staying informed and proactive about cyber insurance will be more important than ever.








