
The Rise of Robotic Process Automation: Transforming Business Operations in the United States
In an era where digital transformation is reshaping industries, robotic process automation (RPA) has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses across the United States. RPA is a form of business process automation that leverages software robots or artificial intelligence agents to perform repetitive tasks with speed and precision. Unlike artificial intelligence, which focuses on learning and decision-making, RPA follows predefined workflows to execute tasks efficiently. This distinction is crucial, as it highlights the unique role RPA plays in streamlining operations without requiring complex AI integration.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation
At its core, RPA is designed to mimic human interactions with digital systems. Instead of relying on traditional programming methods, RPA tools observe users performing tasks within a graphical user interface (GUI) and replicate those actions automatically. This approach allows organizations to automate processes without the need for extensive coding or API integrations. For example, an RPA bot can extract data from an email, input it into a bookkeeping system, and generate a report—all without human intervention.
The benefits of RPA are numerous. It reduces costs, increases efficiency, and enhances accuracy by minimizing errors associated with manual data entry. Additionally, RPA improves scalability, enabling businesses to handle larger volumes of work without proportional increases in staffing. These advantages have made RPA a popular choice for enterprises seeking to optimize their operations.
The Evolution of RPA

While RPA may seem like a modern innovation, its roots trace back to earlier forms of automation such as screen scraping. However, RPA represents a significant evolution in terms of functionality and adaptability. Modern RPA solutions integrate with APIs, ITSM systems, and even AI technologies like image recognition, making them more versatile than their predecessors.
One of the key factors driving RPA adoption is its ability to work with existing systems without requiring major overhauls. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that cannot afford the cost or disruption of implementing new software. By leveraging RPA, companies can extend the life of their current IT infrastructure while still reaping the rewards of automation.
Applications of RPA Across Industries
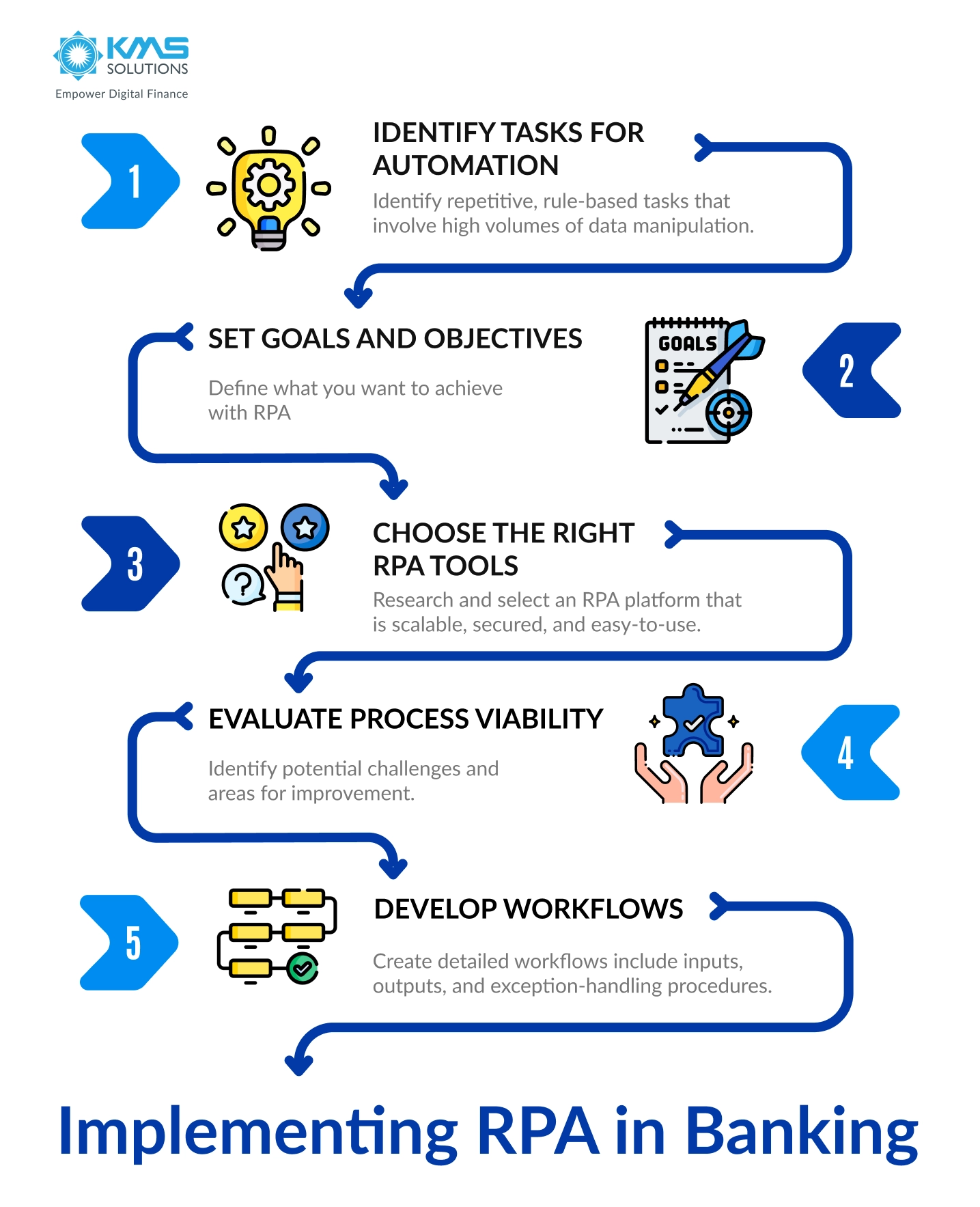
RPA has found applications in a wide range of industries, each benefiting from its ability to streamline operations. In the banking and financial services sector, for instance, RPA is used to automate tasks such as customer research, account opening, and anti-money laundering checks. Major banks have deployed thousands of bots to handle high-volume data entry, significantly reducing processing times and improving accuracy.
In the insurance industry, RPA is employed to manage claims processing, regulatory compliance, and underwriting tasks. These processes often involve repetitive data entry and document verification, which RPA can handle efficiently. Similarly, the retail sector has embraced RPA to enhance back-office operations, including warehouse management, order processing, and fraud detection.
Impact on Employment and Workforce Dynamics
The introduction of RPA has sparked discussions about its impact on employment. While some fear that automation could lead to job losses, many organizations have pledged not to replace employees but rather to redeploy them into more strategic roles. According to studies, knowledge workers often view RPA as a collaborative tool, enhancing their productivity rather than replacing them.
However, the effects of RPA on the business process outsourcing (BPO) industry remain a point of contention. Some analysts argue that RPA could enable companies to “repatriate” offshore processes, potentially reducing opportunities for low-skilled workers in other countries. Conversely, others suggest that RPA may create high-value jobs for skilled professionals in onshore locations.
Challenges and Limitations

Despite its many advantages, RPA is not without challenges. One of the primary limitations is the need for ongoing technical support to adapt to system changes. RPA solutions often require manual reconfiguration when there are updates to the underlying software, which can affect efficiency. Additionally, RPA lacks the autonomy to handle complex, unstructured tasks that require human judgment.
Another challenge is the potential for stifling innovation. As organizations rely heavily on RPA, there is a risk that they may become overly dependent on automated processes, limiting the exploration of new ideas and approaches.
The Future of RPA

Looking ahead, RPA is expected to play an even greater role in the digital transformation of businesses. With advancements in AI and machine learning, RPA is evolving into more sophisticated forms, such as Hyperautomation. This concept combines RPA with other technologies like artificial intelligence and process mining to create more intelligent and adaptive automation solutions.
As businesses continue to seek ways to improve efficiency and reduce costs, RPA will remain a critical component of their strategies. Its ability to integrate with emerging technologies ensures that it will stay relevant in an ever-changing landscape.
Conclusion
Robotic process automation is revolutionizing the way businesses operate in the United States. From streamlining financial processes to enhancing customer service, RPA offers a wide range of benefits that make it an attractive solution for organizations across industries. While challenges exist, the continued evolution of RPA, coupled with its integration with AI and other advanced technologies, ensures that it will remain a vital tool for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital age. As companies embrace automation, they must also consider the broader implications for their workforce and ensure that the transition is managed responsibly.









