The Evolution and Impact of Business Intelligence in Modern Enterprises
Business intelligence (BI) has become a cornerstone of strategic decision-making for organizations across the United States. As companies navigate an increasingly data-driven landscape, BI tools and methodologies have evolved to meet the demands of complex data environments. From historical origins to modern applications, BI plays a pivotal role in transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive business success.
Understanding Business Intelligence
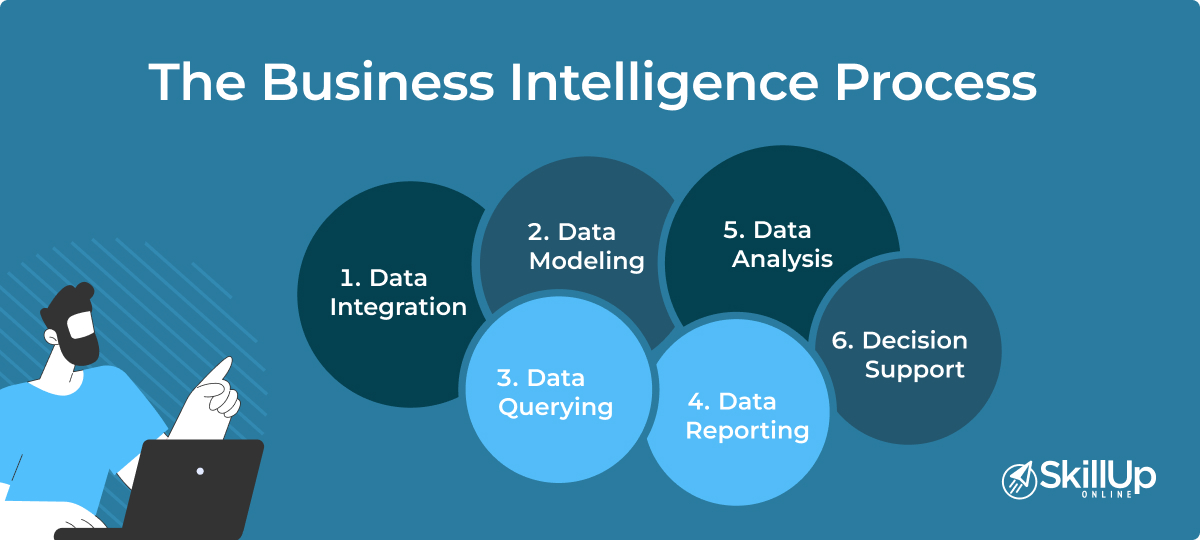
At its core, business intelligence encompasses strategies, methodologies, and technologies used by enterprises to analyze and manage business information. This process enables organizations to make informed decisions by leveraging both structured and unstructured data. Common functions of BI technologies include reporting, analytics, dashboard development, data mining, and predictive analytics. These tools help businesses identify new opportunities, optimize operations, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
BI tools are designed to handle large volumes of data, including structured data from internal systems and unstructured data from sources like social media, emails, and customer feedback. By integrating external market data with internal financial and operational information, BI provides a comprehensive view that supports strategic decision-making. This integration is crucial for understanding market trends, assessing product demand, and evaluating the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
The Historical Development of Business Intelligence
![]()
The concept of business intelligence dates back to the 19th century, with the earliest known use of the term appearing in Richard Millar Devens’ Cyclopædia of Commercial and Business Anecdotes in 1865. Devens described how a banker, Sir Henry Furnese, gained a competitive advantage by acting on timely information about his environment. This early form of BI emphasized the importance of gathering and acting upon relevant data to inform business decisions.
In the mid-20th century, Hans Peter Luhn, a researcher at IBM, further defined the term using the Webster’s Dictionary definition of “intelligence” as “the ability to apprehend the interrelationships of presented facts in such a way as to guide action towards a desired goal.” This conceptualization laid the groundwork for modern BI practices.
By the late 1980s, Howard Dresner introduced the term “business intelligence” as an umbrella term to describe “concepts and methods to improve business decision making by using fact-based support systems.” This definition marked a shift toward more systematic approaches to data analysis and decision-making.
Key Components of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence involves several key components that work together to transform data into insights. These include:
Data Mining
Data mining uses databases, statistics, and machine learning to uncover hidden patterns and trends in large datasets. This process helps organizations identify potential opportunities and risks.
Reporting
Reporting involves sharing data analysis results with stakeholders to facilitate informed decision-making. Effective reports provide clear insights into business performance and areas for improvement.
Performance Metrics and Benchmarking
Comparing current performance data against historical data allows organizations to track progress toward goals. Customized dashboards enable real-time monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs).
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics focuses on understanding what happened by analyzing historical data. This type of analysis provides a foundation for further exploration and forecasting.
Querying
Querying involves asking specific questions about data to retrieve relevant information. BI systems can pull answers from data sets, enabling users to explore various aspects of their business.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis takes descriptive analytics a step further by exploring the underlying reasons for trends and patterns. This process helps organizations understand the factors influencing their performance.
Data Visualization
Data visualization converts complex data into visual representations such as charts, graphs, and histograms. This makes it easier for stakeholders to interpret and act on insights.
Visual Analysis
Visual analysis explores data through visual storytelling, allowing users to communicate insights effectively and stay engaged in the analysis process.
Data Preparation
Data preparation involves compiling multiple data sources, identifying dimensions and measurements, and preparing data for analysis. This step ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and ready for processing.
Business Intelligence vs. Competitive Intelligence and Business Analytics
While business intelligence is often confused with competitive intelligence, there are distinct differences between the two. BI focuses on internal data and processes, while competitive intelligence gathers and analyzes information about competitors. Although competitive intelligence can be considered a subset of BI, it has a narrower focus on market dynamics and competitor strategies.
Similarly, business intelligence and business analytics are sometimes used interchangeably. However, business analytics is typically a subset of BI that focuses on statistical analysis, prediction, and optimization. While BI provides the tools and infrastructure for data analysis, business analytics delves deeper into the interpretation and application of insights.
Challenges and Limitations
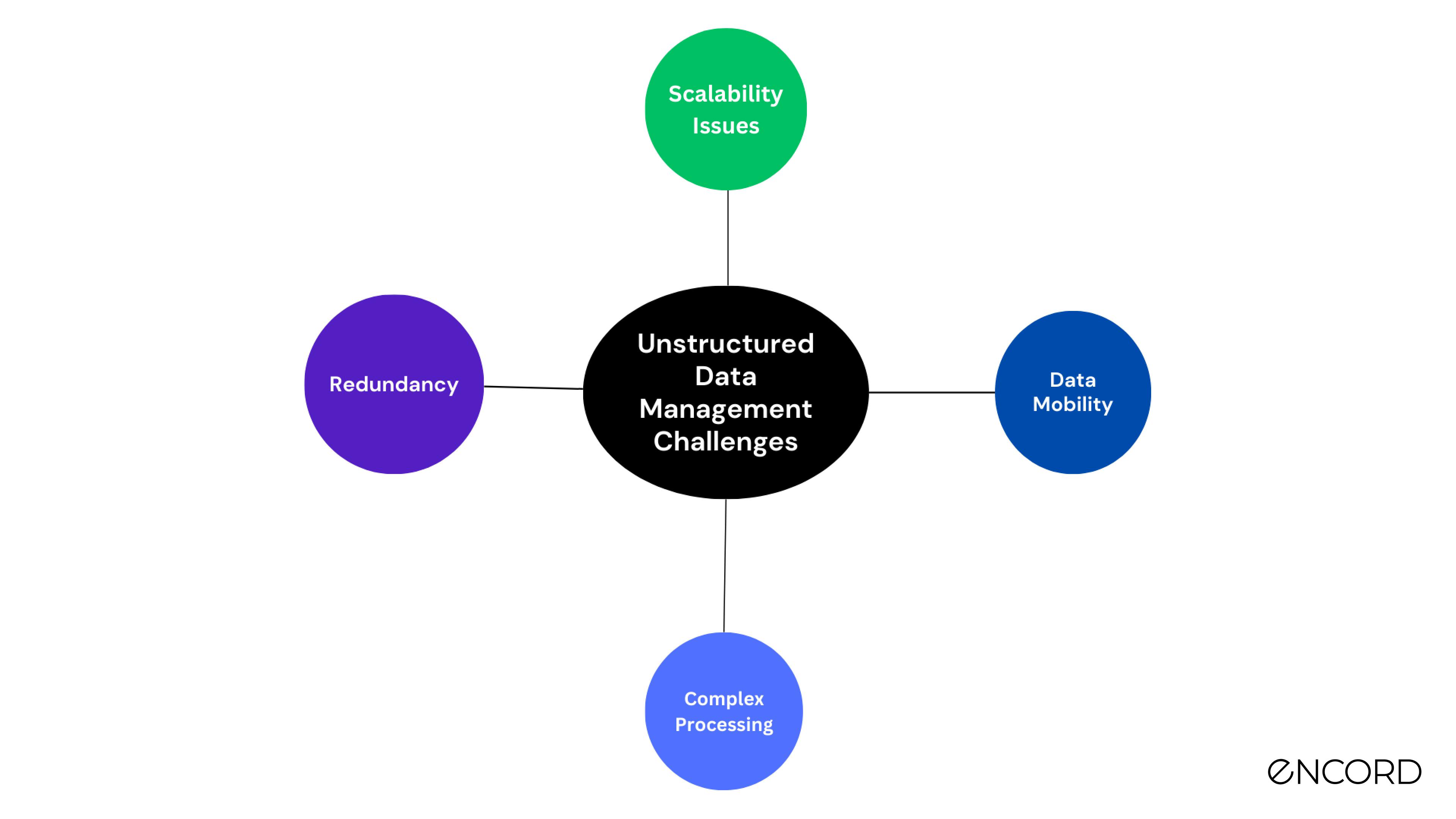
Despite its benefits, business intelligence faces several challenges, particularly when dealing with unstructured and semi-structured data. According to Merrill Lynch, over 85% of business information exists in these formats, including emails, memos, and social media content. Managing this data is complex due to its diverse formats and lack of standardization.
One major challenge is the searchability of unstructured data. Simple keyword searches may miss important context, leading to incomplete or inaccurate insights. To address this, metadata—information about data—plays a critical role in improving searchability and contextual understanding.
The Role of Generative AI in Business Intelligence
Recent advancements in generative artificial intelligence (AI) have transformed the field of business intelligence. Techniques such as large language models enable users to interact with data through natural language queries, generating actionable insights more intuitively. Tools like Microsoft Copilot integrated into Power BI exemplify how generative AI enhances BI capabilities, making data analysis more accessible and efficient.
Applications of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence has a wide range of applications across different industries. In risk management, BI tools help organizations assess potential threats and develop mitigation strategies. For example, the implementation of GDPR in Europe in 2019 forced companies to re-evaluate their data practices, leading to improved compliance and new opportunities for personalized services.
The Future of Business Intelligence

As technology continues to evolve, so does the scope of business intelligence. Modern BI prioritizes self-service analytics and speed to insight, empowering users to customize dashboards and create reports independently. This shift from traditional, top-down approaches to interactive, user-centric models has made BI more accessible and dynamic.
In conclusion, business intelligence is an essential tool for organizations seeking to leverage data for strategic advantage. By combining advanced technologies, robust data management practices, and a focus on user empowerment, BI continues to shape the future of decision-making in the United States and beyond.








