Asset Management in the United Kingdom: A Comprehensive Guide
Asset management is a critical component of the financial and operational strategies of organizations, whether they are private, public, or non-profit. In the United Kingdom, this practice plays a vital role in ensuring that assets—both tangible and intangible—are maintained, optimized, and utilized effectively to achieve long-term goals. This article explores the concept of asset management, its various forms, and its significance within the UK context.
What is Asset Management?
At its core, asset management refers to the systematic process of managing and maintaining an organization’s assets to maximize their value and utility over time. These assets can be physical, such as buildings, machinery, and infrastructure, or intangible, like intellectual property, software, and brand equity. The primary objective of asset management is to ensure that these resources are used efficiently, sustainably, and in alignment with organizational objectives.
In the UK, asset management is not only a financial strategy but also a governance mechanism. It involves making informed decisions about the acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal of assets. This approach helps organizations reduce costs, mitigate risks, and improve performance across all sectors.
Types of Asset Management
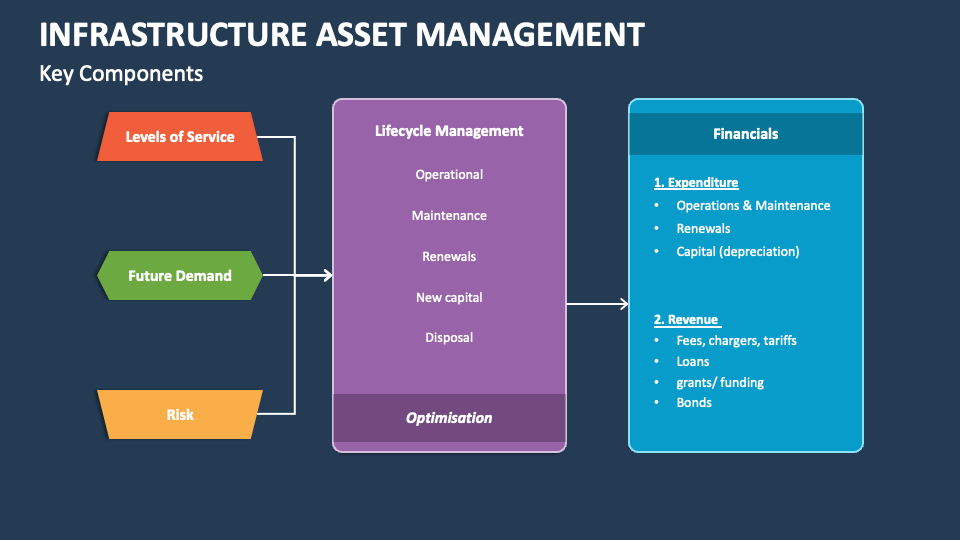
There are several distinct types of asset management, each tailored to specific needs and industries. Understanding these categories can help organizations determine the most effective approach for their operations.
-
Financial Asset Management
Financial asset management focuses on managing investments, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, on behalf of clients. In the UK, this includes portfolio managers who oversee investment funds and individual accounts. Financial asset managers aim to grow wealth while managing risk, often using active or passive strategies. Active management involves frequent trading and analysis, while passive management follows market indices. -
Physical and Infrastructure Asset Management
This type of asset management deals with the lifecycle of physical assets, including design, construction, operation, maintenance, and disposal. In the UK, it is particularly relevant for public infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and utilities. Effective physical asset management ensures that these assets remain functional, safe, and cost-effective over their lifespan. -
Engineering Asset Management
Engineering asset management is a specialized field that combines engineering principles with financial and risk management practices. It is commonly used in industries such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation. Engineers and asset managers work together to optimize the performance of complex systems, ensuring reliability and efficiency. -
Software and Digital Asset Management
With the rise of digital transformation, software and digital asset management have become increasingly important. These strategies involve managing digital assets, such as data, software licenses, and multimedia content, to ensure security, compliance, and efficient use. -
Natural Asset Management
Natural asset management involves the sustainable use and conservation of natural resources, such as forests, water bodies, and agricultural land. In the UK, this is gaining traction as organizations seek to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Key Principles of Asset Management
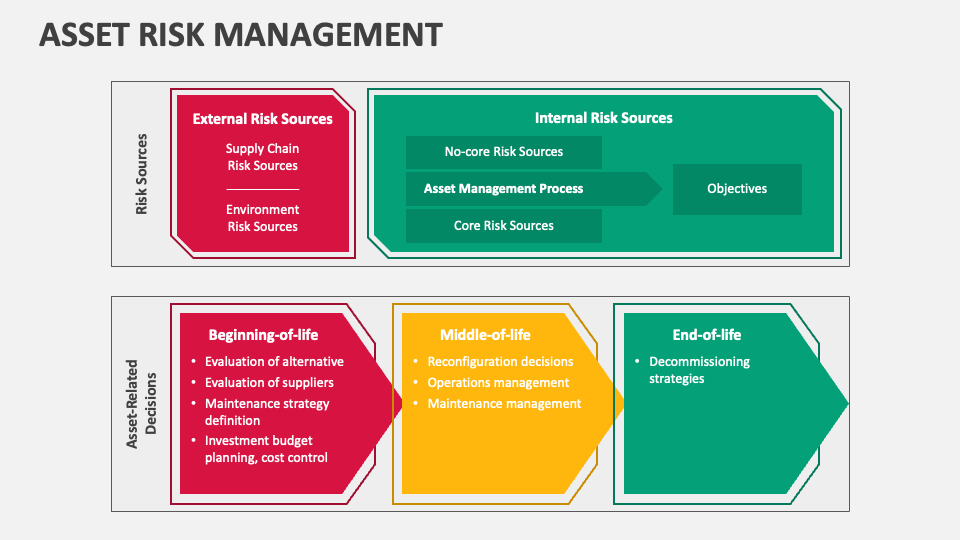
To implement effective asset management, organizations must adhere to several key principles:
- Lifecycle Management: Assets should be managed throughout their entire lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with asset failure, obsolescence, or underperformance is essential.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Balancing the costs of maintaining and upgrading assets with their benefits is crucial.
- Sustainability: Ensuring that asset management practices align with environmental and social responsibilities.
- Compliance: Adhering to legal and regulatory requirements related to asset ownership, usage, and disposal.
The Role of Standards in Asset Management
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed the ISO 55000 series of standards to provide a framework for effective asset management. These standards define best practices for managing physical and intangible assets, emphasizing the importance of strategic planning, continuous improvement, and stakeholder engagement.
In the UK, many organizations adopt these standards to ensure consistency and quality in their asset management processes. The ISO 55001 standard, for example, outlines the requirements for an asset management system, while ISO 55002 provides guidance on its implementation.
Challenges and Opportunities in UK Asset Management
Despite its benefits, asset management in the UK faces several challenges, including:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many public infrastructure assets in the UK are aging and require significant investment for maintenance and upgrades.
- Technological Disruption: The rapid pace of technological change necessitates continuous adaptation of asset management strategies.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating the evolving regulatory landscape can be challenging for organizations.
However, there are also numerous opportunities, such as:
- Digital Transformation: Leveraging technology to improve asset tracking, monitoring, and decision-making.
- Sustainable Practices: Embracing green initiatives to enhance the value of natural and physical assets.
- Collaboration: Partnering with other stakeholders, such as government agencies and private sector firms, to share resources and expertise.
Conclusion
Asset management is a multifaceted discipline that plays a vital role in the success of organizations across the UK. By adopting a systematic and strategic approach, businesses and public institutions can optimize their assets, reduce costs, and achieve long-term sustainability. As the UK continues to evolve, the importance of effective asset management will only grow, offering new opportunities for innovation and growth.









