
Azure Security Best Practices: A Comprehensive Guide for U.S. Organizations
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cloud security has become a top priority for organizations across the United States. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure, it is essential to implement robust security measures that protect sensitive data and infrastructure. This article explores key Azure security best practices and patterns, offering insights into how IT professionals can design, deploy, and manage secure cloud solutions.
Understanding Azure Security Best Practices
Azure security best practices are designed to help IT professionals—such as designers, architects, developers, and testers—build and deploy secure cloud environments. These guidelines are derived from Microsoft’s extensive experience with Azure security and the real-world challenges faced by customers. By following these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyber threats and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Key Components of Azure Security
- Security Posture Visibility: As the cloud environment expands, the likelihood of breaches going unnoticed increases. Tools that provide visibility into your security posture are crucial for proactive management.
- Cloud Security Policies: Defining organization-wide security policies helps enforce restrictions and maintain consistency across cloud deployments.
- Container Security: With Kubernetes being a popular orchestration platform, securing containers involves creating standard baselines and using advanced technologies for monitoring.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Continuous scanning and remediation services are necessary to protect workloads against malware and other threats.
- Zero Trust Approach: This approach assumes that no entity is trusted by default, even within the organization’s network, and requires strict access controls and monitoring.
Enhancing Security Posture Visibility

To effectively manage cloud security, organizations must have tools that provide visibility into their security posture. Leading cloud platforms offer native Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) solutions with advanced features such as detecting data exfiltration, event threats, IAM account hijacks, and cryptomining. However, these tools may be limited to specific cloud platforms.
For hybrid or multi-cloud environments, specialized tools are recommended to ensure comprehensive security posture visibility. These tools can detect anomalies and provide actionable insights to mitigate risks before they escalate.
Implementing Cloud Security Policies

Organizations should define clear cloud security policies to enforce restrictions and ensure compliance. For example, policies can limit workload deployment using public IPs, control east-west traffic flow, or monitor container workload traffic patterns.
In Azure, customers can leverage Azure policies to automate compliance checks. Similarly, Google Cloud users can utilize organizational policies. The advantage of these policies is that they enforce compliance standards across all cloud deployments, reducing the risk of misconfigurations and unauthorized access.
Securing Containers in the Cloud

With the increasing adoption of containerization, securing containers has become a critical aspect of cloud security. Kubernetes is the most commonly used orchestration platform, and securing it involves creating industry-standard security baselines.
Tools that detect malicious activities in containers, even during runtime, are essential. These tools should also enable visibility into container-related activities and allow for the detection and decommissioning of rogue containers. Advanced AI and machine learning (ML) technologies can enhance threat detection without relying solely on signatures.
Performing Vulnerability Assessments and Remediation
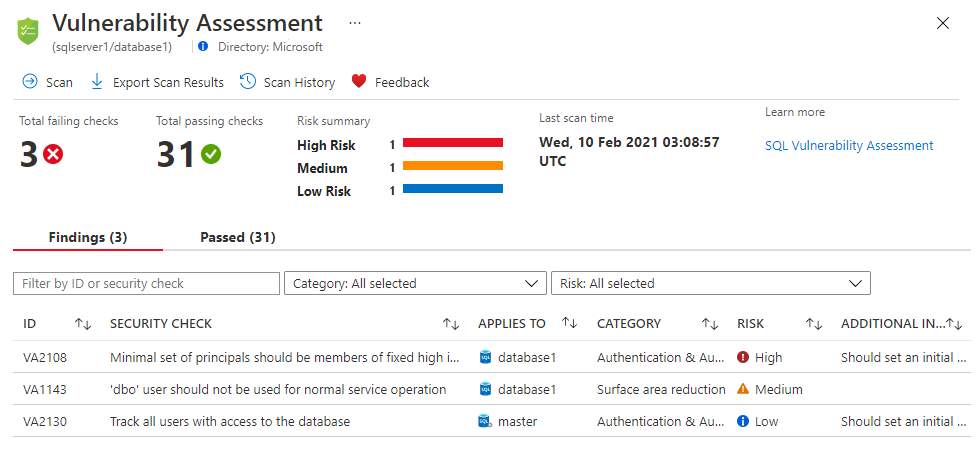
A real-time vulnerability scanning and remediation service is vital for protecting workloads against malware and other threats. These services should support both virtual machines (VMs) and containerized workloads.
Consider implementing a vulnerability management solution that continuously scans for vulnerabilities, compiles reports, and presents results in dashboards. Auto-remediation capabilities can quickly address issues, minimizing the window of exposure.
Adopting a Zero Trust Approach

The Zero Trust model, often referred to as “assume breach,” is considered the gold standard for cloud security. It involves not assuming any trust between services, even those within the organization’s network.
Key principles of Zero Trust include segmentation, minimal communication between services, and strict access controls. All communications, including admin activities, should be monitored, logged, and analyzed for anomalies. Organizations can use native or third-party tools to implement this approach effectively.
Collaborative Efforts in Cloud Security
In addition to individual efforts, collaborative initiatives play a significant role in enhancing cloud security. For instance, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Security Agency (NSA) have released joint Cybersecurity Information Sheets (CSIs) to provide best practices and mitigations for securing cloud environments.
These CSIs encourage organizations to review and implement the recommended practices to strengthen their cloud security. Additional resources, such as CISA’s Secure Cloud Business Applications (SCuBA) Project and Trusted Internet Connections (TIC) pages, offer further guidance on cloud security best practices.
Conclusion
As organizations continue to embrace cloud computing, ensuring robust security measures is more critical than ever. By following Azure security best practices, leveraging advanced tools, and adopting a Zero Trust approach, U.S. organizations can significantly enhance their cloud security posture. Staying informed about the latest developments and collaborating with agencies like CISA and NSA will further support these efforts, helping to create a safer and more resilient digital ecosystem.









