Navigating the Insurance Claim Process: A Comprehensive Guide for UK Policyholders
Insurance claims can often feel like a daunting process, especially when you’re dealing with the aftermath of an unexpected event. Whether it’s a car accident, property damage, or a health emergency, understanding how to navigate the insurance claim process is essential. This guide will walk you through each step, from filing a claim to receiving your payout, ensuring that you are well-prepared and informed throughout the process.
What is an Insurance Claim?
An insurance claim is a formal request made by a policyholder to their insurance company for payment or reimbursement for a loss or damage covered under their policy. It serves as a crucial mechanism to access the financial protection you’ve paid for through your premiums. The primary purpose of filing a claim is to recover financially from a covered loss, whether it’s repairs to your vehicle, medical bills, or rebuilding your home after a disaster.
Before You File: Essential Preparations
Before you even consider filing a claim, there are several steps you should take to ensure a smooth process:
- Review Your Policy: Understand what is covered and what is excluded. Check the “Coverages” section and be aware of any specific “Exclusions.” Also, note your policy limits and deductible amounts.
- Gather Key Information and Documentation: For property damage, collect photos, police reports, witness information, and other relevant documents. For medical claims, gather provider information, diagnosis codes, and medical records.
Understanding your deductible is also crucial. If the repair cost is close to or less than your deductible, it might not be worth filing a claim, as it could impact future premiums.
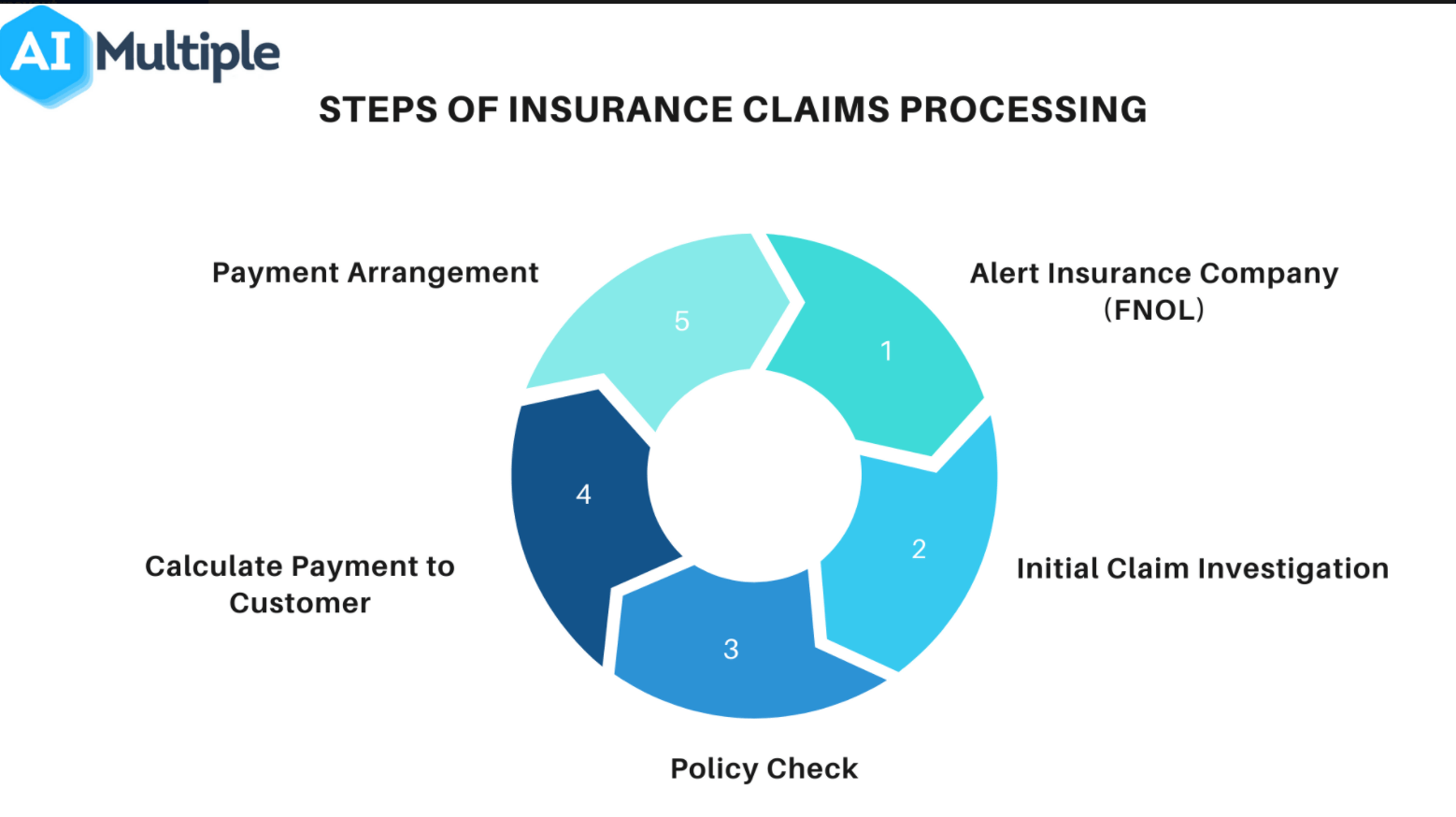
Step-by-Step: The Insurance Claim Process Explained
While the specifics can vary slightly by insurer and claim type, the general flow of the insurance claim process follows a predictable sequence:
- Reporting the Loss (Filing the Claim): Report the loss as soon as possible. Contact your insurer through their online portal, phone, or agent. Provide your policy number, basic details of the incident, and your contact information.
- Claim Number and Adjuster Assignment: Once your claim is reported, you’ll receive a unique claim number. An insurance adjuster will be assigned to your claim to investigate the loss and assess damages.
- Investigation and Documentation by the Adjuster: The adjuster will gather all necessary facts to evaluate the claim. They may visit the scene of the loss, interview witnesses, and review records.
- Damage Assessment and Estimation: Based on their investigation, the adjuster will assess the extent of the covered damage and estimate the cost of repairs or replacement.
- Reviewing the Settlement Offer: The insurer will make a settlement offer. Review it carefully and compare it against your own estimates. If you disagree, provide documentation to support your position.
- Receiving Your Payout and Repairs: Upon agreement, the insurer will issue the payment. For property claims, proceed with repairs or replacement and keep receipts.
What If Your Claim is Denied or Disputed?
If your claim is denied or you dispute the settlement offer, knowing your options is crucial. Common reasons for denials include exclusions in your policy, lapsed coverage, or insufficient documentation. You can request a detailed explanation, provide additional documentation, or pursue internal appeals. If necessary, you can also file a complaint with your state’s Department of Insurance.
Tips for a Smoother Claims Experience
To enhance your experience, document everything from photos of the damage to records of phone calls. Communicate clearly and consistently with your insurer, and be patient yet persistent. Understanding your rights as a policyholder in the UK is also important.
Types of Insurance Claims
There are various types of insurance claims, each with its own process:
- Car Insurance Claims: Include collisions, property damage, and incidents involving uninsured drivers.
- Homeowners Insurance Claims: Cover structural damage, injuries, and personal property damage.
- Renter’s Insurance Claims: Address theft, damage to personal property, and injuries in rented properties.
- Life Insurance Claims: Involve the payment to beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death.
How Insurance Claims Work
Filing an insurance claim typically involves checking your policy details, gathering information, and submitting the claim to your insurer. Payment is usually issued to you or the service provider, depending on the nature of the claim.
The Insurance Claim Life Cycle
The life cycle starts with the First Notice of Loss (FNOL) and ends with resolution—either payment or denial. Understanding each stage helps set realistic expectations and keeps your claim moving forward.
Realistic Timelines
The duration of a claim varies by state and complexity. Most states give insurers about 30 days to make a decision after receiving all necessary information. However, timelines can extend for complex cases or during catastrophes.
Your Responsibilities vs. The Insurer’s
For your claim to proceed smoothly, report promptly, prevent further damage, and document your loss thoroughly. Your insurer must conduct a reasonable investigation, communicate regularly, and pay undisputed amounts promptly.
Disputes and Your Options
Disagreements happen, and you have several options, including appraisal clauses, mediation, and arbitration. Understanding these processes can help resolve disputes effectively.
Money Mechanics
Deductibles come first, followed by the assessment of Actual Cash Value (ACV) versus Replacement Cost Value (RCV). Undisputed amounts are paid promptly, while disputed portions are investigated further.
Tech That Speeds Things Up
Modern technology has transformed claims handling, with digital FNOL, AI-powered assessments, and real-time tracking. These advancements streamline the process and improve efficiency.
After Settlement: Subrogation, Salvage, Recovery
Subrogation allows your insurer to seek reimbursement from responsible parties. Salvage refers to damaged property taken by the insurer after paying to replace it.
FAQs
Common questions include how long insurers have to investigate, what to do if you disagree with an estimate, and the role of the Special Investigation Unit (SIU). Understanding these can help you navigate the process more confidently.
By following this comprehensive guide, you can confidently navigate the insurance claim process, ensuring a smoother experience and the full benefit of your coverage. Remember, your insurance policy is a crucial financial tool; knowing how to activate its protection effectively ensures you receive the full benefit you’ve paid for.








