
The Evolution and Impact of Cloud Computing in the United States
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses, governments, and individuals access and manage technology. From its conceptual origins in the 1960s to its current dominance in the digital landscape, cloud computing has evolved into a critical infrastructure for modern operations. In the United States, this transformation has been particularly significant, shaping industries, enabling innovation, and redefining how data is stored, processed, and shared.
Understanding Cloud Computing
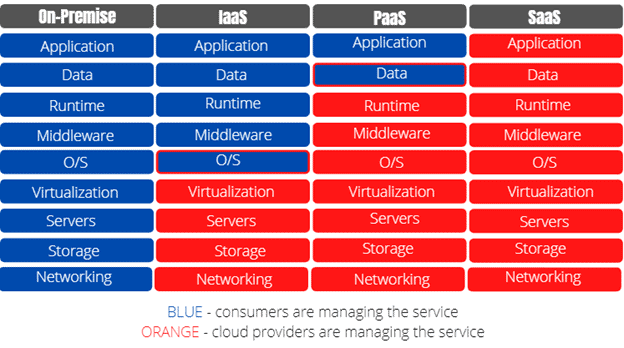
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). This model allows users to access these resources on-demand without the need for physical hardware or local infrastructure. Instead, third-party providers host and manage the necessary systems, offering scalable and flexible solutions that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
The key components of cloud computing include:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform allowing customers to develop, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis, with the provider managing all aspects of the software.
The Rise of Cloud Services in the U.S.
The journey of cloud computing in the United States began in the late 20th century, with early concepts like time-sharing and remote job entry. However, it wasn’t until the 2000s that cloud computing started gaining traction. Amazon Web Services (AWS), launched in 2002, marked a pivotal moment in the industry. It introduced services like Amazon S3 and EC2, which allowed developers to build and scale applications independently.
By the mid-2010s, other major players such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud emerged, creating a competitive market that drove innovation and expanded the range of available services. Today, the U.S. remains a global leader in cloud computing, with companies like AWS, Microsoft, and Google dominating the market. These providers offer not only basic infrastructure but also advanced tools for artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics.
Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Adoption

The adoption of cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. Businesses can avoid the upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure, instead paying only for the resources they use. This pay-as-you-go model enables organizations to scale their operations up or down based on demand, making it ideal for startups and rapidly growing companies.
However, the transition to the cloud is not without challenges. Security and privacy concerns remain a top priority, as sensitive data is stored and managed by third-party providers. Organizations must ensure that their cloud providers adhere to strict security protocols and compliance standards, such as GDPR and HIPAA. Additionally, the complexity of cloud environments can lead to issues like misconfigurations, which may result in data breaches or service outages.
Another challenge is the potential for vendor lock-in, where businesses become heavily dependent on a single cloud provider, making it difficult to switch services. To mitigate this risk, many organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy, using services from multiple providers to maintain flexibility and reduce dependency.
The Future of Cloud Computing in the U.S.

As cloud computing continues to evolve, new trends are emerging that will shape its future. One of the most significant developments is the rise of edge computing, which brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. This approach reduces latency and improves performance, making it ideal for applications that require real-time processing, such as autonomous vehicles and IoT devices.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into cloud platforms is transforming the way businesses operate. These technologies enable organizations to analyze vast amounts of data, uncover insights, and automate processes, leading to increased efficiency and innovation.
In the coming years, the U.S. is expected to see continued growth in cloud adoption, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for digital services, and the need for more agile and scalable solutions. As the cloud becomes more integral to everyday life, its impact on the economy, society, and individual users will only continue to expand.








