
The Evolution and Importance of Data Engineering in the Modern Enterprise
Data engineering has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, enabling organizations to harness the power of data for strategic decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage. As enterprises generate and collect vast amounts of data from diverse sources, the need for robust data infrastructure, efficient processing pipelines, and scalable storage solutions has never been greater. This article explores the evolution of data engineering, its key components, and its critical role in today’s data-driven world.
The Origins of Data Engineering
The concept of data engineering can be traced back to the 1970s and 1980s with the emergence of information engineering methodology (IEM). Developed by pioneers like Clive Finkelstein and James Martin, IEM aimed to bridge the gap between business planning and information systems. These early techniques were designed to help database administrators (DBAs) and systems analysts create structured data systems that aligned with organizational goals. Over time, as businesses became more data-centric, the focus shifted from traditional database design to broader data management practices.
In the early 2000s, data was primarily managed by IT teams, with limited collaboration across departments. However, the rise of the internet and the explosion of data volumes in the 2010s led to the creation of the term “data engineer”. Companies like Google, Facebook, and Netflix began investing heavily in data infrastructure, moving away from traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes toward more advanced data engineering practices. This shift emphasized cloud computing, real-time processing, and scalable data architectures.
Key Components of Data Engineering
Data engineering encompasses several critical components that ensure data is collected, stored, processed, and made available for analysis. These include:
1. Data Collection
Data engineers gather raw data from various sources such as databases, APIs, sensors, and logs. This step is crucial as the quality and completeness of the data directly impact subsequent processes.
2. Data Storage
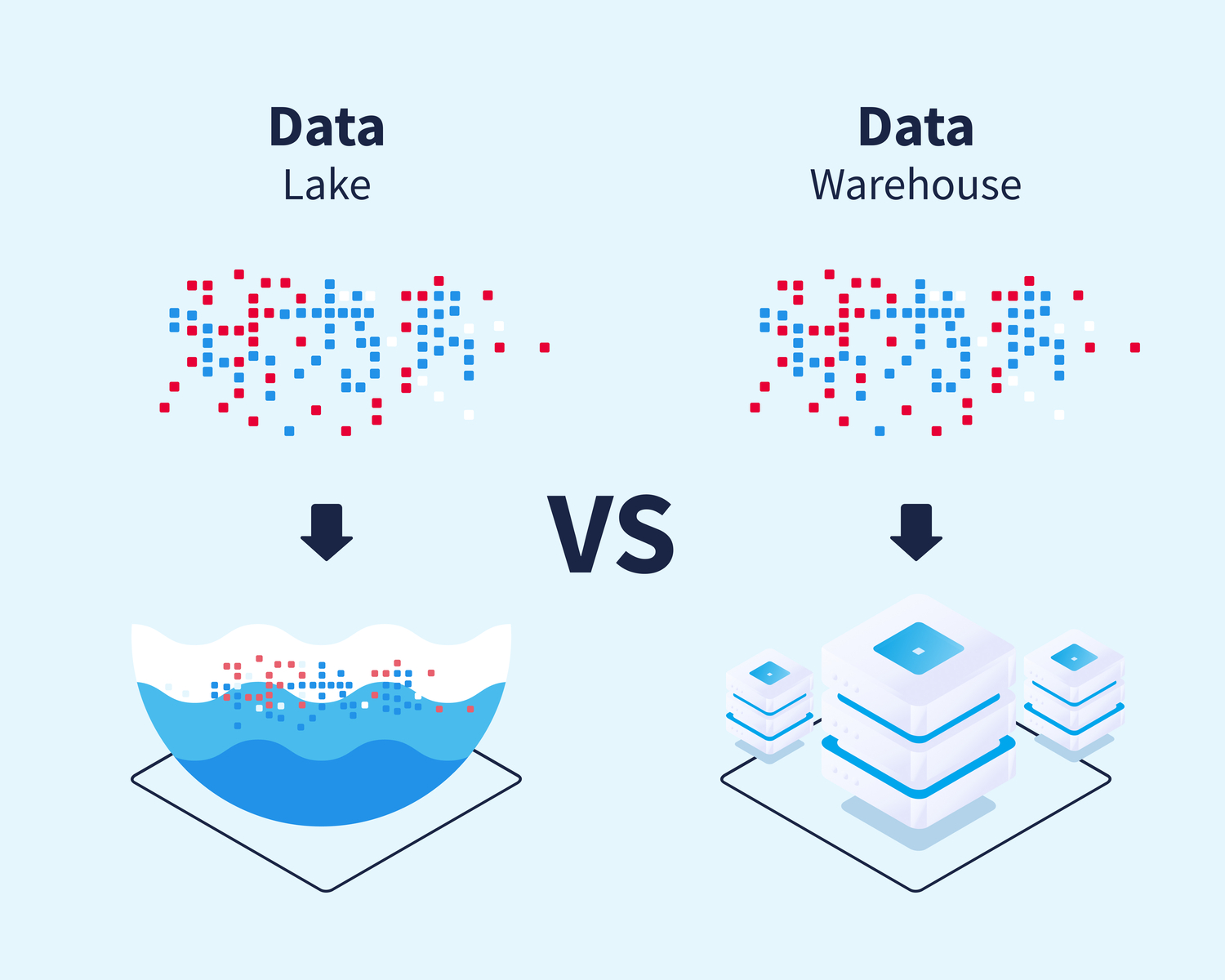
Once data is collected, it must be stored in a manner that allows for efficient retrieval and processing. Data engineers design and manage storage solutions such as data warehouses, data lakes, and databases. These solutions must balance performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
3. Data Processing
Data processing involves transforming raw data into a structured and usable format. This includes data cleaning, normalization, and integration. Tools like Apache Spark, Hadoop, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) frameworks are commonly used to automate and optimize these processes.
4. Data Pipelines
Data pipelines are automated workflows that move data from source to destination, ensuring that data flows smoothly and consistently. They encompass data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), as well as real-time data streaming. Effective pipeline management is essential for maintaining data integrity and availability.
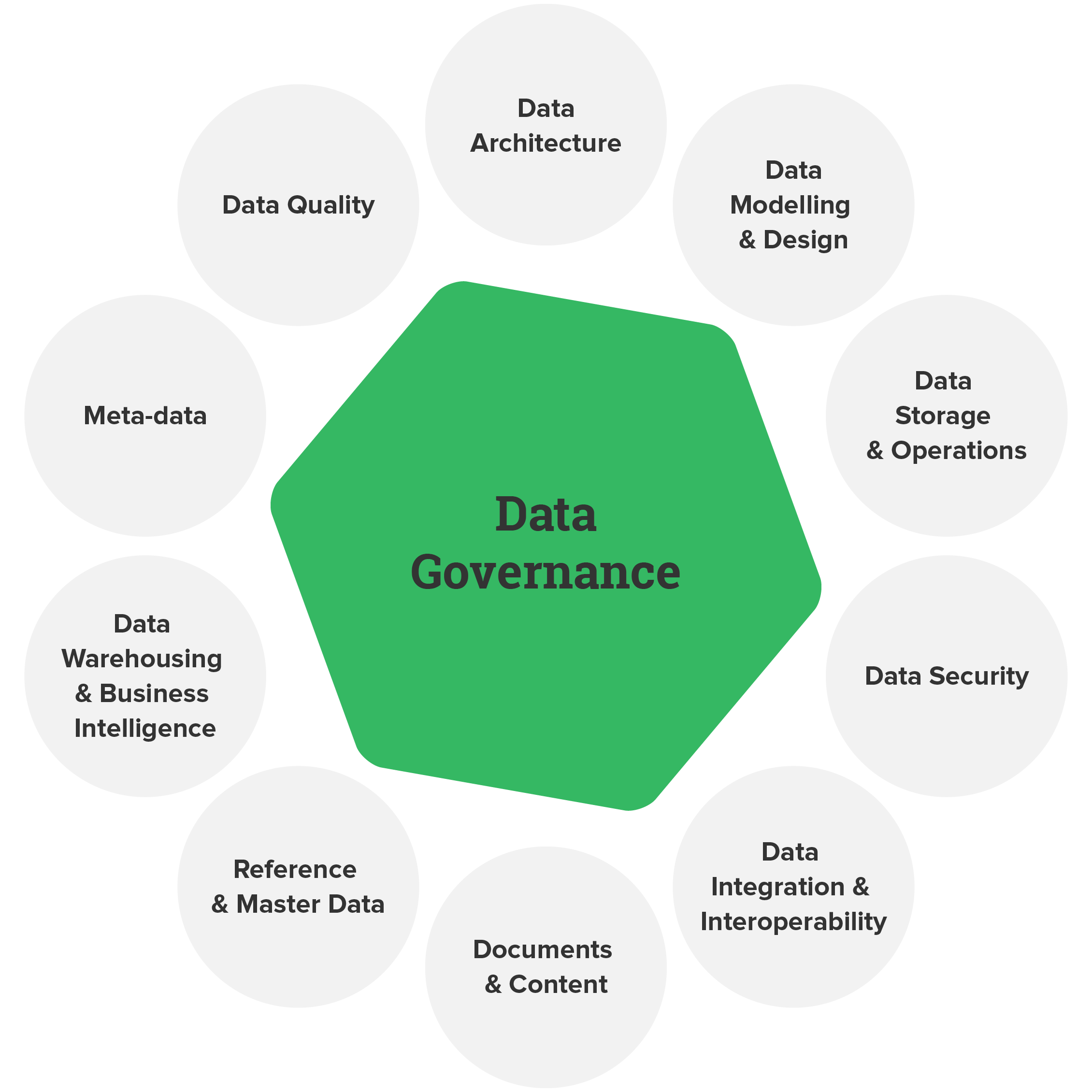
5. Data Quality and Governance
Ensuring data quality and governance involves implementing policies and procedures to maintain data accuracy, consistency, and security. Data engineers establish data validation checks, monitor data for anomalies, and enforce compliance with data privacy regulations.


Why Data Engineering Matters
Data engineering forms the backbone of any data-driven enterprise. It ensures that data is accurate, reliable, and accessible, providing a solid foundation for data analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence applications. Without effective data engineering, organizations may struggle with data inconsistencies, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies, hindering their ability to derive meaningful insights.
Moreover, data engineering plays a vital role in supporting data science and analytics. By preparing and pre-processing data for professionals in these fields, data engineers enable the development of predictive models, recommendation systems, and other advanced analytics tools. This not only enhances decision-making but also drives innovation and growth.
Challenges in Data Engineering
Despite its importance, data engineering is not without its challenges. Some of the most common issues include:
- Handling Large Volumes of Data: Managing and processing large datasets efficiently requires specialized tools and techniques.
- Ensuring Data Quality: Maintaining high data quality across diverse sources can be complex.
- Scalability: Building systems that can scale with growing data volumes and user demands.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data from breaches and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Keeping Up with Technology: Rapid advancements in technology require data engineers to continually update their skills and knowledge.
Data Engineering vs. Data Science
While data engineering and data science are closely related, they serve distinct roles within the data ecosystem. Data engineering focuses on building and maintaining the infrastructure needed to process and store data, while data science is concerned with analyzing data to extract insights and build predictive models.
| Aspect | Data Engineering | Data Science |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Data infrastructure, pipelines, and processing | Data analysis, modeling, and insights |
| Objective | Prepare, transform, and manage data for use | Extract insights, build predictive models |
| Data Handling | Raw data cleaning, integration, storage | Analyzing, exploring, visualizing data |
| Tools and Technologies | Apache Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, SQL/NoSQL databases | Python/R, Jupyter Notebooks, Machine Learning libraries |
| Skills | Programming (Python, Java), ETL, database management | Statistics, Machine Learning, Data Visualization |
| Output | Clean, structured data ready for analysis and reporting | Predictive models, insights, actionable recommendations |
Future Trends in Data Engineering
The field of data engineering is continually evolving, with several emerging trends shaping its future:
- DataOps: An extension of DevOps, focusing on improving collaboration and automation in data workflows.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Increasing demand for real-time analytics and decision-making capabilities.
- Machine Learning Operations (MLOps): Integrating machine learning models into data pipelines for seamless deployment and management.
- Cloud-Native Data Engineering: Leveraging cloud platforms for scalable and cost-effective data solutions.
- Data Privacy and Ethics: Growing emphasis on data privacy, ethical data usage, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Conclusion
In conclusion, data engineering is the foundation of modern data-driven enterprises. It enables organizations to collect, store, process, and analyze vast amounts of data from diverse sources, ensuring that the data is accurate, reliable, and accessible for strategic decision-making. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, the role of data engineers will only become more critical. By addressing the challenges and embracing emerging trends, data engineers will continue to play a pivotal role in driving innovation and success in the digital age.








