The Future of Communication: Understanding Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is one of the most transformative branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI), revolutionizing how machines interact with human language. From text generators that compose coherent essays to chatbots that mimic human conversation, NLP has become a cornerstone of modern technology. Its applications span across industries, including healthcare, finance, and customer service, making it an essential tool for businesses and individuals alike. As AI continues to evolve, NLP’s role in shaping the future of communication is becoming more profound.
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
At its core, NLP is the science of enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It involves analyzing both written and spoken language, extracting meaning from it, and using that understanding to perform tasks like translation, sentiment analysis, and text generation. NLP combines elements of linguistics, computer science, and machine learning to create systems that can process and respond to natural language inputs in a way that feels intuitive to humans.
NLP is typically divided into two main subfields: Natural Language Understanding (NLU), which focuses on interpreting the meaning of text, and Natural Language Generation (NLG), which involves creating human-like responses. These two components work together to enable machines to engage in meaningful conversations with users.
Why Does NLP Matter?
NLP plays a critical role in everyday life, often without users even realizing it. Virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri rely on NLP to understand and respond to voice commands. Search engines such as Google use NLP to deliver more accurate and contextually relevant results. Social media platforms employ NLP to detect and filter harmful content, while healthcare providers use it to analyze patient records and improve diagnostics.
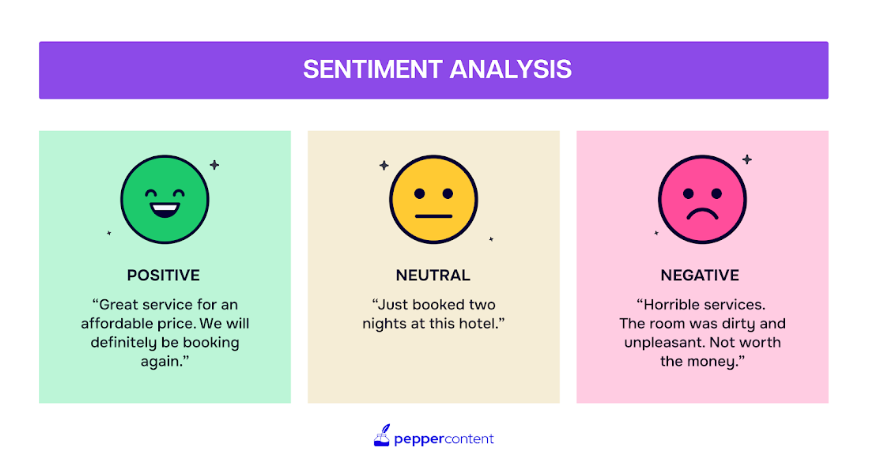
The growing sophistication of NLP has also led to advancements in areas like machine translation, where systems like Google Translate break down language barriers. In addition, text summarization tools help users quickly digest large volumes of information, while sentiment analysis enables businesses to gauge customer opinions and preferences.
Despite its many benefits, NLP still faces challenges. Current models can be biased or produce incoherent outputs, and they often struggle with understanding sarcasm, idioms, and nuanced expressions. However, ongoing research and development are addressing these issues, paving the way for more accurate and reliable NLP systems.
What is NLP Used For?
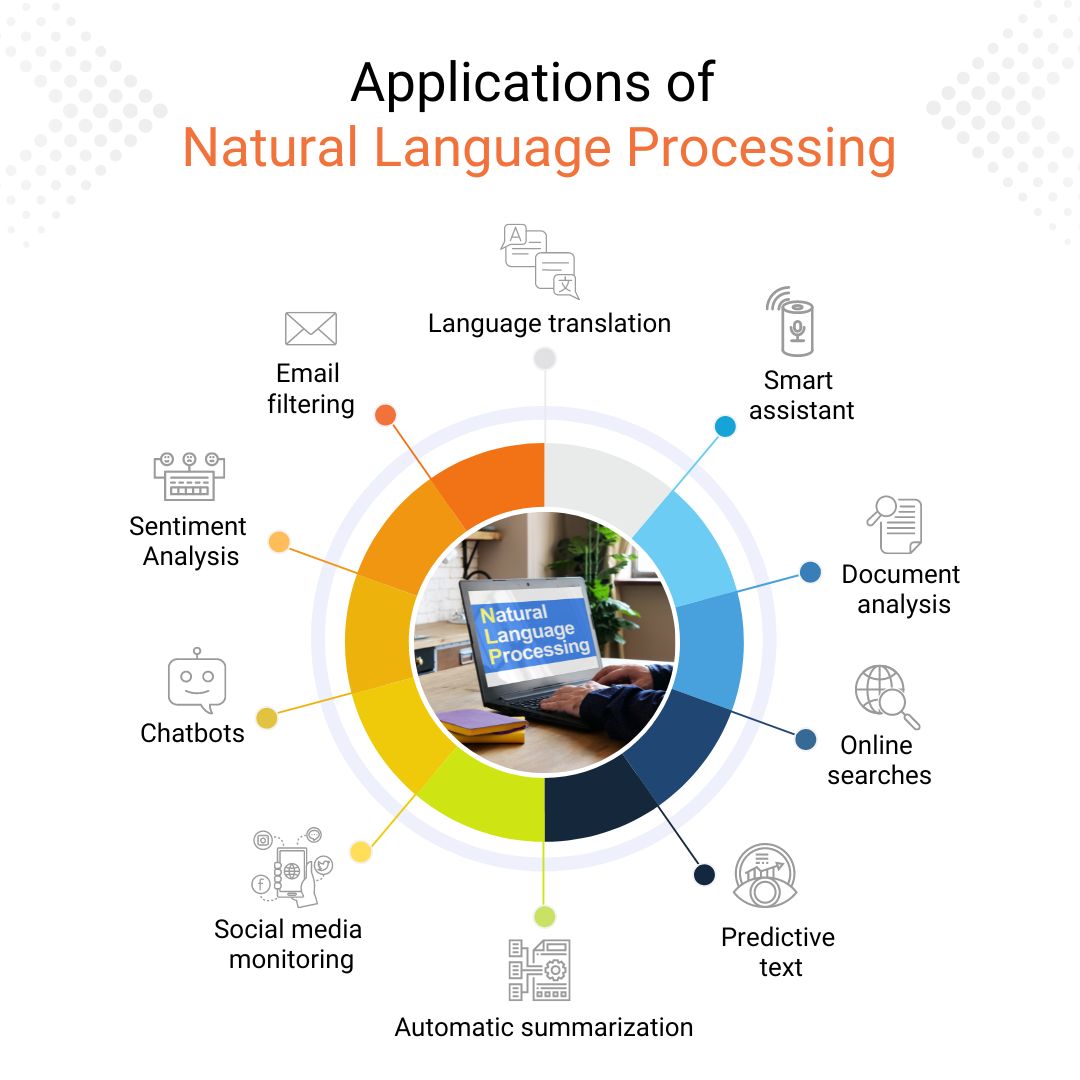
NLP is used for a wide range of tasks, each designed to enhance the interaction between humans and machines. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Sentiment Analysis: Identifies the emotional tone of text, such as positive, negative, or neutral.
- Toxicity Classification: Detects harmful content like hate speech or threats.
- Machine Translation: Converts text from one language to another.
- Named Entity Recognition: Extracts key entities such as names, locations, and organizations.
- Spam Detection: Filters out unwanted emails and messages.
- Grammatical Error Correction: Helps users improve their writing by identifying and correcting errors.
- Topic Modeling: Identifies themes or topics within a collection of documents.
- Text Generation: Creates human-like text for purposes like article writing or chatbot responses.
- Information Retrieval: Finds relevant documents based on user queries.
- Summarization: Condenses long texts into shorter, more manageable summaries.
- Question Answering: Provides answers to user questions in natural language.
These tasks are made possible through advanced algorithms and deep learning models that continuously improve as they process more data.
How Does NLP Work?
NLP systems work by breaking down language into smaller components and analyzing them to extract meaning. This process involves several key steps:
- Data Preprocessing: Text is cleaned and transformed into a format that machines can understand. Techniques like stemming, lemmatization, and tokenization help simplify and standardize the input.
- Feature Extraction: Words and phrases are converted into numerical representations, such as Bag-of-Words, TF-IDF, or word embeddings like Word2Vec and GloVe.
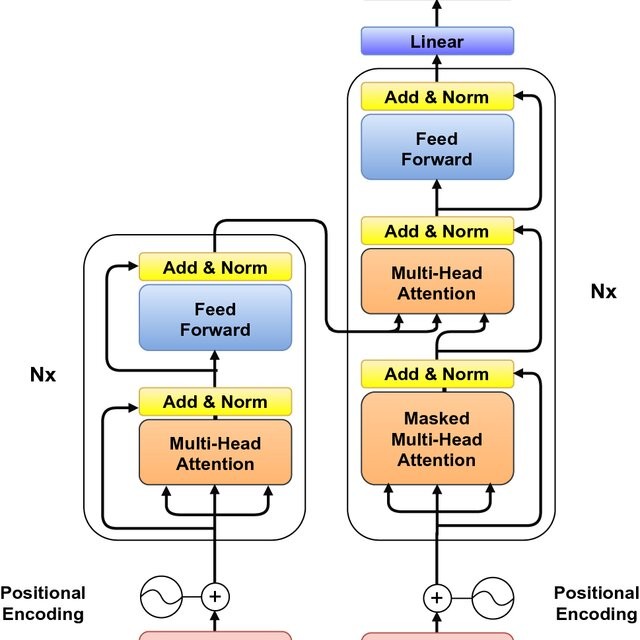
- Modeling: Machine learning or deep learning models are trained on the processed data to perform specific tasks. Traditional models like logistic regression and decision trees are used alongside more complex architectures like recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers.
The transformer architecture, introduced in 2017, has been particularly influential, enabling models like BERT and GPT-3 to achieve state-of-the-art performance in various NLP tasks.
Top NLP Techniques
Several techniques are commonly used in NLP, ranging from traditional machine learning methods to advanced deep learning approaches:
- Traditional Methods: Include logistic regression, Naive Bayes, decision trees, and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) for topic modeling.
- Deep Learning Methods: Involve convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), autoencoders, and transformers.
Each technique has its strengths and is suited for different types of tasks. For example, transformers have proven highly effective in tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as question answering and language translation.
Notable NLP Models
Several groundbreaking NLP models have shaped the field, including:
- Eliza: One of the earliest chatbots, developed in the 1960s.
- Tay: A Microsoft chatbot that learned from user interactions but was later shut down due to inappropriate behavior.
- BERT: A pre-trained model that has significantly improved performance in various NLP tasks.
- GPT-3: A massive language model capable of generating human-like text.
- LaMDA: A conversational AI developed by Google that sparked debates about AI sentience.
These models demonstrate the rapid progress in NLP and highlight the potential for future innovations.
Programming Languages and Tools
Python is the most widely used programming language for NLP, thanks to its rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Some of the most popular tools include:
- NLTK: A library for building NLP applications.
- spaCy: An open-source library for advanced NLP tasks.
- Hugging Face: A platform offering pre-trained models and tools for NLP development.
- TensorFlow and PyTorch: Deep learning frameworks used for building NLP models.
Other languages like R and Java also have NLP libraries, though Python remains the dominant choice for most practitioners.
Controversies and Challenges
While NLP has brought many benefits, it is not without controversy. Concerns include:
- Bias and Discrimination: NLP models can inherit biases from their training data, leading to unfair outcomes.
- Environmental Impact: Training large NLP models requires significant computational resources, contributing to carbon emissions.
- Ethical Issues: Questions about AI sentience, as seen with LaMDA, raise philosophical and ethical debates.
- Accessibility: High costs and technical complexity can limit access to NLP tools for smaller organizations.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring that NLP develops responsibly and equitably.
Getting Started with NLP
For those interested in learning NLP, there are numerous resources available:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses on NLP and AI.
- Research Papers: Reading foundational papers helps deepen understanding of NLP concepts.
- Open Source Projects: Contributing to or studying open-source NLP projects provides hands-on experience.
Starting with basic algorithms like linear regression and logistic regression can build a strong foundation before moving on to more complex models.
Conclusion
Natural Language Processing is reshaping the way we interact with technology, making it more intuitive and accessible. From virtual assistants to advanced chatbots, NLP is driving innovation across industries. While challenges remain, the continued development of NLP promises to unlock new possibilities for communication, automation, and decision-making.
As the field advances, it is essential to address ethical concerns and ensure that NLP benefits society as a whole. With its vast potential, NLP is set to play an even greater role in our daily lives, bridging the gap between humans and machines in ways we are only beginning to imagine.