The Future of Software Testing: A Comprehensive Guide to SaaS Testing in the United States
In today’s digital age, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) has become a cornerstone of modern software development. Unlike traditional software models, SaaS applications are hosted on the cloud and accessed via the internet, allowing users to enjoy seamless, scalable, and secure solutions. However, with this shift comes the need for rigorous testing to ensure these applications perform reliably across diverse environments. This article delves into the world of SaaS testing, exploring its importance, challenges, and the tools that make it possible.
What is SaaS Testing?
SaaS testing refers to the process of evaluating the performance, security, and usability of cloud-hosted software applications. It involves testing from the end-user perspective to ensure the application functions effectively across different devices, browsers, and environments. The primary goal of SaaS testing is to guarantee that the software meets its intended objectives, provides a consistent user experience, and remains secure and scalable under varying conditions.
Why SaaS Testing Matters
SaaS testing is crucial for several reasons:
- Improves User Experience: By validating functionality and usability, SaaS testing ensures users have a smooth and consistent experience.
- Verifies Scalability: It confirms the application can handle increased load and traffic without compromising performance.
- Assures Data Security: SaaS testing identifies vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with industry standards.
- Enhances Customer Satisfaction: Delivering a bug-free, high-performance product leads to higher customer satisfaction.
- Improves Application Maintainability: Ensuring stable updates and feature releases makes maintenance easier.
Types of SaaS Testing

There are several types of SaaS testing, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Manual Testing
Manual testing involves human testers executing test cases to assess usability, exploratory scenarios, and subjective elements. While time-consuming, it allows for real-life scenario testing that automated tools may miss.
2. Automated Testing
Automated testing uses software tools and scripts to verify functionality without manual intervention. It is ideal for repetitive tasks and large-scale checks, saving time in the long run.
3. Functional Testing
Functional testing verifies that the SaaS application performs its intended functions correctly and meets business requirements.
4. Performance Testing
Performance testing assesses how well the application performs under various loads, checking speed, stability, and scalability.
5. Security Testing
Security testing identifies vulnerabilities and ensures the application is protected against potential threats.
6. Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates the user experience to ensure the application is easy to navigate and intuitive.
7. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing ensures the SaaS application works seamlessly across different devices, browsers, and operating systems.
8. Regression Testing
Regression testing confirms that new updates or changes do not negatively impact existing functionality.
Challenges in SaaS Testing
Despite its benefits, SaaS testing comes with unique challenges:
- Testing Across Multiple Browsers, Devices, and Operating Systems: Ensuring consistent functionality across all platforms is a complex task.
- Verifying Application Performance Under Varying User Loads: Handling high traffic and network conditions requires robust testing strategies.
- Ensuring Compatibility with Frequent Updates: New features and updates must be tested without introducing regressions.
- Testing Third-Party Integrations and APIs: Ensuring consistency across different platforms and services is critical.
- Managing Multi-Tenant Environments: Data isolation and user-specific configurations must be thoroughly tested.
Manual vs. Automation Testing: Choosing the Right Approach
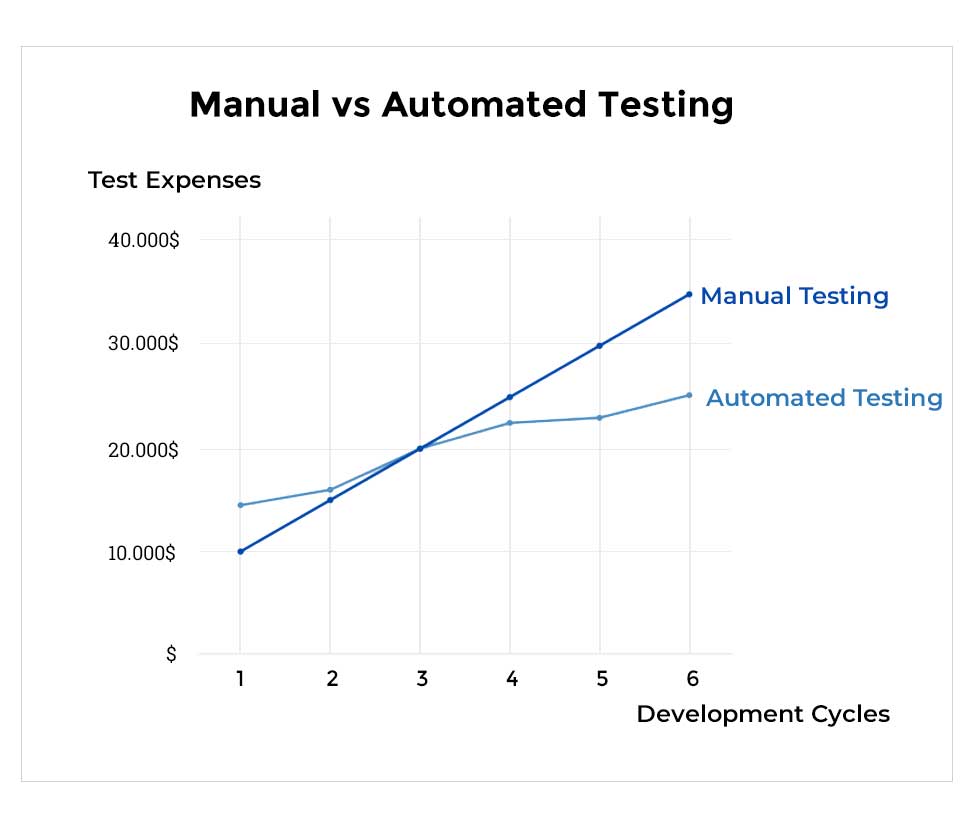
When deciding between manual and automation testing, consider the following factors:
Manual Testing
- Pros: High probability of detecting human errors, provides a high-end user experience, and is suitable for exploratory and usability testing.
- Cons: Time-consuming, less efficient for repetitive tasks, and requires skilled testers.
Automation Testing
- Pros: Faster execution, lower chance of errors, and ideal for regression and performance testing.
- Cons: Requires initial investment in scripting, and not all tests can be automated.
SaaS Testing Methodology
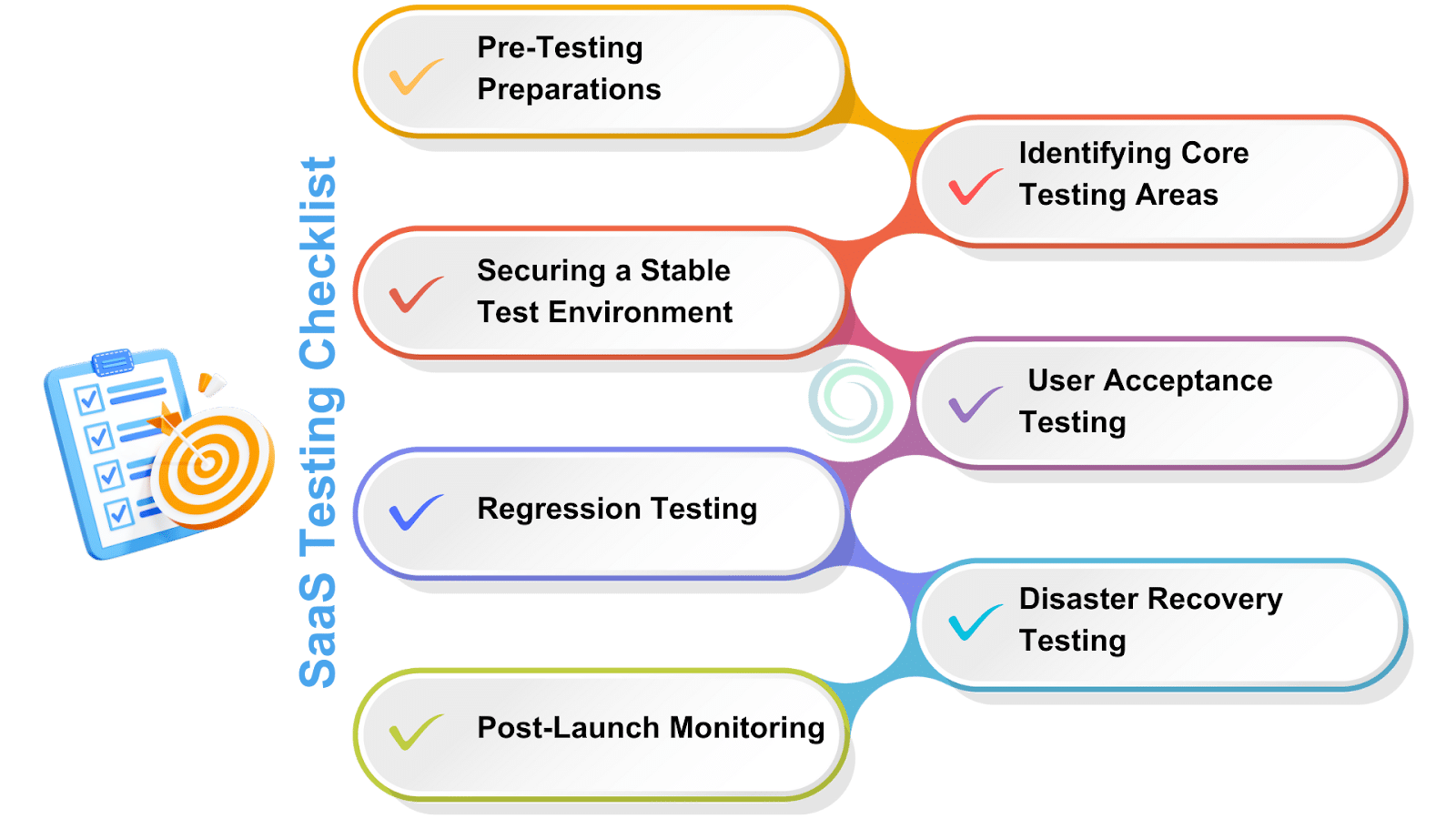
A structured approach to SaaS testing is essential for success. The main steps include:
1. Planning
- Requirement Analysis: Understand and document the application’s specific requirements.
- Test Environment Setup: Prepare a test environment mirroring the production setup.
- Test Case Design: Create comprehensive test plans covering all aspects.
- Data Preparation: Ensure diverse and realistic test data availability.
2. Execution
- Functional Testing: Verify that the application functions as intended.
- Performance Testing: Assess the application’s performance under various conditions.
- Security Testing: Evaluate the application’s security through penetration and vulnerability testing.
- Usability Testing: Ensure a user-friendly experience.
- Regression Testing: Continuously test for new issues with updates and bug fixes.
3. Analysis
- Result Evaluation: Analyze results and document any issues.
- Root Cause Analysis: Understand why issues occurred.
- Prioritization: Rank issues by severity.
- Re-testing: Confirm issue resolution without introducing new defects.
SaaS Testing Tools

Several tools are available to streamline the SaaS testing process. Some of the most popular ones include:
1. LambdaTest
LambdaTest is an AI-native test orchestration and execution platform that allows testing on 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations. It offers features like cross-browser testing, automation testing, and real device testing.
2. Selenium
Selenium is an open-source tool that supports multiple programming languages and enables automation testing for web applications. It is compatible with various browsers and operating systems.
3. Cypress
Cypress is known for its fast, real-time, end-to-end testing of web applications. It excels in simulating user actions, making it ideal for ensuring smooth user experiences in SaaS environments.
4. Appium
Appium is a versatile tool for automating native, hybrid, and web applications across iOS and Android platforms. It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
5. New Relic
New Relic is a powerful tool for monitoring and managing digital performance. It helps track and enhance software application performance, providing insights into metrics that matter most.
Best Practices for SaaS Testing

To overcome the challenges of SaaS testing, consider the following best practices:
- Check Compatibility with Diverse Platforms: Ensure the application works across various devices and browsers for every release.
- Understand Application Complexity: Recognize the features, integrations, and user interactions involved.
- Focus on Key Testing Types: Prioritize security, performance, and user interface testing based on the application’s functionality.
- Use SaaS Testing Tools: Leverage tools like LambdaTest, Selenium, and Cypress to streamline the testing process.
- Collaborate with Agile Teams: Work closely with feature teams to align testing with development cycles.
- Strategize Testing: Align testing strategies with organizational and project objectives.
- Perform Security Testing: Regularly check for vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Execute Performance Testing: Prioritize performance testing to ensure the application can handle high traffic and loads.
Conclusion
SaaS testing is a critical component of modern software development, ensuring that cloud-based applications perform reliably, securely, and efficiently. With the right approach and tools, organizations can overcome the challenges of SaaS testing and deliver high-quality products that meet user expectations. Whether you choose manual or automation testing, the key is to find a balance that suits your application’s needs and goals.
As the demand for SaaS applications continues to grow, effective testing tools and methodologies will play an increasingly important role in ensuring their success. By staying informed about the latest trends and best practices, developers and testers can navigate the complexities of SaaS testing and deliver exceptional user experiences.








