The Ultimate Guide to Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in the United States
In today’s fast-paced tech landscape, launching a successful product requires more than just a great idea—it demands strategic execution. A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the cornerstone of this process, allowing startups and entrepreneurs to test their concepts with real users before investing heavily in full-scale development. Understanding how long it takes to build an MVP and what factors influence the timeline is crucial for any business aiming to enter the market efficiently.
The typical timeframe for building an MVP ranges from 3 to 4 months, depending on the project’s complexity and scope. However, foundational versions can take 6 to 12 months, while highly complex MVPs may require up to 24 months. This article explores the key phases of MVP development, factors that affect timelines, and practical strategies to accelerate the process.
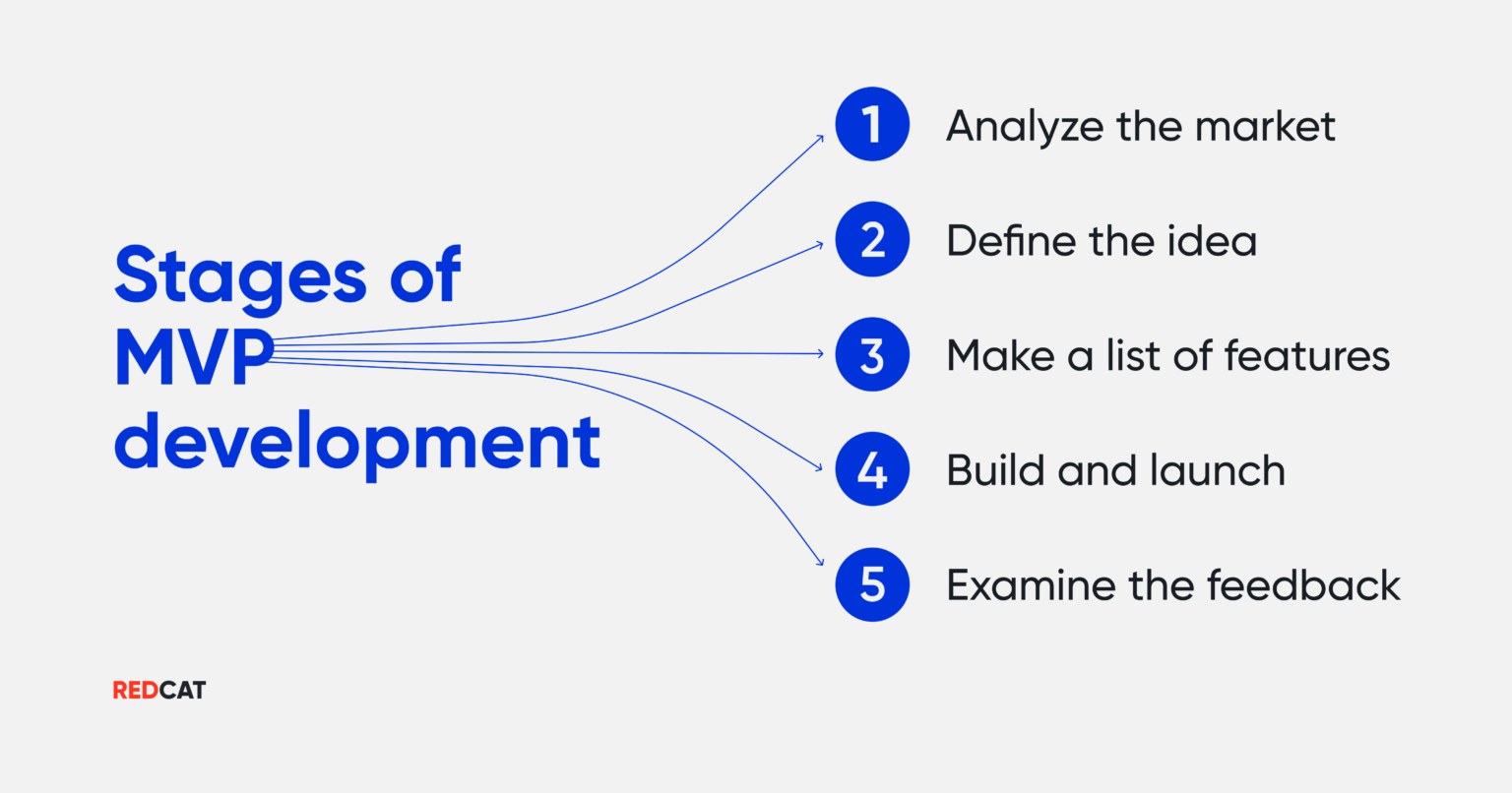
Key Phases in MVP Development
The MVP development process is structured into five critical phases: Ideation and Planning, Design and Prototyping, Development, Testing, and Deployment. Each phase plays a vital role in ensuring the final product meets user needs and aligns with business goals.
Ideation and Planning
The first step involves identifying the core problem your product will solve and conducting thorough market research. This phase typically takes 1-2 weeks and includes defining the MVP’s scope, prioritizing features, and outlining a roadmap. Tools like pain and gain maps help identify essential features that directly address user pain points.
Design and Prototyping
Once the problem is defined, the next step is designing a user-friendly interface. UI/UX design focuses on creating an intuitive experience that aligns with user expectations. This phase usually lasts 7-10 days and involves wireframing, prototyping, and gathering feedback to refine the product’s look and feel.
Development Phase

The development phase is where the core functionalities of the MVP are built. Frontend and backend development typically takes 4-8 weeks, depending on the project’s complexity. Challenges such as integrating third-party services or managing technical debt can extend this timeline.
Testing Processes
Thorough testing ensures the MVP is reliable and performs well under various conditions. This phase includes user acceptance testing (UAT), performance testing, and bug fixing. It usually takes 1-2 weeks but can vary based on the product’s requirements.
Deployment Phase

The final step is deploying the MVP to the market. This phase involves setting up landing pages, configuring servers, and ensuring the product is ready for real-world use. Deployment typically takes 10-14 days and marks the beginning of user feedback collection.
Factors Influencing MVP Development Time
Several factors impact the time required to build an MVP:
- Project Scope and Complexity: A well-defined scope avoids unnecessary delays. Complex features and frequent changes in requirements can prolong the timeline.
- Team Experience and Skills: An experienced team can significantly reduce development time by anticipating challenges and solving problems efficiently.
- Technology Stack: Choosing the right tools and frameworks, such as Flutter for mobile apps, can streamline the development process and speed up delivery.
- Market Research and Business Model: Thorough market analysis helps identify user needs and ensures the MVP aligns with the target audience.
Real-World Examples of MVP Timelines
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how different industries approach MVP development. For instance, Candis’ invoice processing app was delivered within 16 weeks, demonstrating the efficiency of focused development. Similarly, a food ordering app prototype using Flutter was completed in two months, highlighting the benefits of modern technology stacks.
These examples show that with proper planning and execution, even complex MVPs can be developed quickly and effectively.
How to Speed Up MVP Development

To accelerate the MVP development process, consider the following strategies:
Prioritize Essential Features
Focus on the core functionalities that directly solve the user’s problem. Techniques like the MoSCoW method (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) help prioritize features and avoid feature bloat.
Utilize Agile Methodologies
Agile practices emphasize iterative development, regular feedback, and continuous improvement. By breaking the project into smaller sprints, teams can adapt quickly to changes and maintain momentum.
Leverage Pre-Built Solutions
Using pre-built APIs, SDKs, and libraries can save time and reduce development costs. Tools like UXPin Merge allow designers to create interactive prototypes that closely resemble the final product, streamlining the development process.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is essential for a smooth MVP journey. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
Scope Creep
Expanding the project scope mid-development can lead to delays and budget overruns. Establish clear boundaries early to maintain focus and control.
Insufficient Testing
Neglecting thorough testing can result in undetected bugs and poor user experiences. Implement robust testing processes to ensure the MVP is reliable and user-friendly.
Post-Launch Activities
After deployment, the work isn’t over. Continuous feedback collection, user testing, and iterative improvements are crucial for refining the product and meeting evolving user needs.
Feedback Collection
Gather user feedback through surveys, interviews, and analytics tools. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and guide future iterations.
Iterative Improvements
Based on user insights, refine the product and prioritize new features. This ongoing process ensures the MVP evolves to meet market demands and stay competitive.
Summary
Building an MVP is a strategic process that requires careful planning, efficient execution, and continuous refinement. By understanding the key phases, influencing factors, and best practices, startups can develop a product that meets user needs and lays the foundation for long-term success.
Whether you’re launching a mobile app, SaaS platform, or web-based solution, the principles outlined in this guide can help you navigate the MVP development journey with confidence. Remember, the goal of an MVP is not to create a perfect product but to learn and iterate based on real-world feedback.










