The Ultimate Guide to Financial Literacy: Build a Stronger Financial Future
Financial literacy is more than just knowing how to balance a checkbook. It’s a crucial life skill that empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their money, manage debt, and plan for the future. In today’s complex financial landscape, understanding personal finance is essential for achieving long-term stability and success. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to improve your current financial situation, this guide will provide you with the tools and knowledge needed to take control of your financial future.
Understanding Your Current Finances
The first step in building financial literacy is to understand where you stand financially. This involves taking stock of your income, expenses, debts, and savings. Start by listing all your sources of income, including your salary, side gigs, and any passive income streams. Next, track your monthly expenses, categorizing them into essentials (rent, utilities, groceries), debt payments (credit cards, student loans), and discretionary spending (entertainment, dining out).
Creating a detailed budget is also essential. A budget helps you allocate your money effectively and ensures that you’re not overspending. There are various budgeting methods to choose from, such as the 50/30/20 rule, which divides your income into 50% for essentials, 30% for discretionary spending, and 20% for savings and debt repayment. Alternatively, zero-based budgeting assigns every dollar a purpose, giving you total control over your finances.
Setting Clear Financial Goals

Once you have a clear picture of your finances, the next step is to define your financial goals. These goals can be short-term, medium-term, or long-term. Short-term goals might include saving for a vacation or paying off a credit card balance, while long-term goals could involve buying a home, funding an education, or retiring comfortably.
It’s important to set specific, measurable, and achievable goals. For example, instead of saying “I want to save money,” set a goal like “I want to save $3,000 for a down payment on a car in 12 months.” This provides a clear target and timeline, making it easier to track your progress.
Prioritize your goals based on urgency and importance. Some goals may require immediate attention, such as paying off high-interest debt, while others can be pursued gradually, like building a retirement fund.
Creating a Realistic Budget
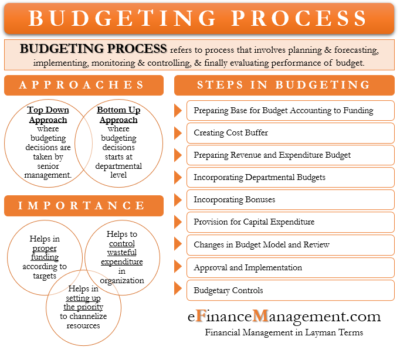
A realistic budget is the foundation of effective financial management. Start by allocating funds for essential expenses such as housing, food, utilities, and transportation. Then, plan for debt repayment and savings contributions. Finally, assign money for discretionary spending.
Creating a budget requires honesty and flexibility. Overly strict budgets can be difficult to maintain, while overly lenient ones may fail to produce meaningful progress. Experiment with different budgeting methods to find one that works best for you.
Building an Emergency Fund

Unexpected expenses can disrupt your financial progress. An emergency fund provides a safety net for events such as medical bills, car repairs, or temporary unemployment. Aim to save three to six months of living expenses in an accessible account. If this target seems daunting, start with a smaller goal, such as $500 or $1,000, and build gradually from there.
Place your emergency fund in a separate account to avoid the temptation to spend it on non-emergencies. High-yield savings accounts can offer interest while keeping the money liquid. If you do have a true emergency and need to dip into your fund, replenish it as soon as you can. Having an emergency fund in place reduces stress and prevents the need for high-interest borrowing in times of financial difficulty.
Saving and Investing for the Future
After establishing an emergency fund, focus on long-term savings and investments. Retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, are valuable tools because they offer tax advantages and allow for compound growth over time. Take full advantage of employer matching contributions whenever they’re available.
Beyond retirement, college funds, real estate investments, and entrepreneurial ventures can also benefit from dedicated investment accounts. Consider investing in a diverse array of stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and index funds that align with your risk tolerance and financial timeline. Diversification reduces the impact of market fluctuations and provides potential growth over decades.
Reviewing and Improving Your Plan
Life circumstances, income levels, and goals can evolve over time, and regularly reviewing your plan can help ensure that it continues to reflect your current situation. Schedule a review of your finances once a year. Evaluate your spending, debt, savings, and investments, and adjust your budget or goals as necessary.
Utilizing tools like financial apps or spreadsheets can simplify this process. Over time, minor adjustments and consistent monitoring can yield substantial improvements in your financial stability and confidence.
Resources for Financial Education

Educating yourself about money matters is essential, but if you’re already struggling with money, you certainly don’t want to spend big on financial literacy courses. Fortunately, there are numerous free or inexpensive online resources available to help you learn the fundamentals of personal finance.
Courses such as “Personal Finance 101” and “Financial Basics Everyone Should Know” provide a solid foundation in budgeting, debt management, and savings. Additionally, platforms like Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, and Khan Academy offer a wide range of courses on topics such as taxes, investing, and retirement planning.
Conclusion
Financial literacy is a critical skill that empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their money, manage debt, and plan for the future. By understanding your current finances, setting clear goals, creating a realistic budget, building an emergency fund, and investing for the future, you can take control of your financial destiny. With the right tools and resources, anyone can develop the financial knowledge and confidence needed to achieve long-term stability and success.










