The Ultimate Guide to Kubernetes: Everything You Need to Know
Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s, has become a cornerstone in the world of container orchestration. Developed initially by Google and now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), Kubernetes is an open-source platform designed to automate deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. As more organizations adopt cloud-native strategies, understanding Kubernetes becomes essential for developers, DevOps engineers, and IT professionals.
Understanding the Need for Kubernetes
The rise of microservices architecture and containerization has made it increasingly complex to manage applications across multiple environments. Traditional methods of deploying applications on single servers or even a few hosts are no longer sufficient for handling the dynamic demands of modern software. This is where Kubernetes steps in, offering a robust solution to manage containers at scale.
Real-World Examples
Consider a scenario where you have a Java application that needs to be deployed. Using Docker, you can package the application into a container and run it on a server with a Docker engine. However, this setup presents a single point of failure. If the server goes down, your application is unavailable. Kubernetes addresses this issue by enabling you to scale applications across multiple nodes, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance.
Another example involves a large application composed of multiple microservices. Each microservice must communicate with others, which introduces complexities in networking, load balancing, and service discovery. Kubernetes simplifies these challenges by providing a framework to manage these interactions seamlessly.
Core Features of Kubernetes
Kubernetes offers a comprehensive set of features that make it a powerful tool for managing containerized applications:
Application-Centric Management
Kubernetes focuses on treating applications as top priorities, making it easier to configure and run them automatically. This approach ensures that your applications are always running as intended.
Automated Deployment and Scaling
One of the most significant benefits of Kubernetes is its ability to automatically adjust workloads based on demand. Whether your application experiences a surge in traffic or a drop, Kubernetes can scale up or down accordingly, optimizing resource utilization.
Self-Healing Capabilities
Kubernetes automatically detects failed containers and replaces or restarts them, ensuring that the system remains healthy. This self-healing feature minimizes downtime and maintains the desired state of your applications.
Portability Across Environments
Kubernetes abstracts the underlying infrastructure, allowing applications to run consistently across different environments, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid setups. This portability is crucial for organizations looking to leverage multi-cloud strategies.
Getting Started with Kubernetes
For those new to Kubernetes, starting with a structured learning path is essential. The following sections outline key areas to focus on when beginning your journey with Kubernetes.
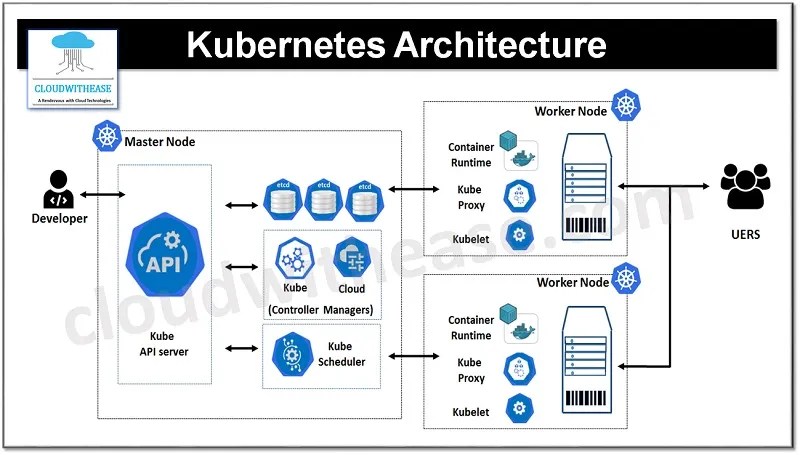
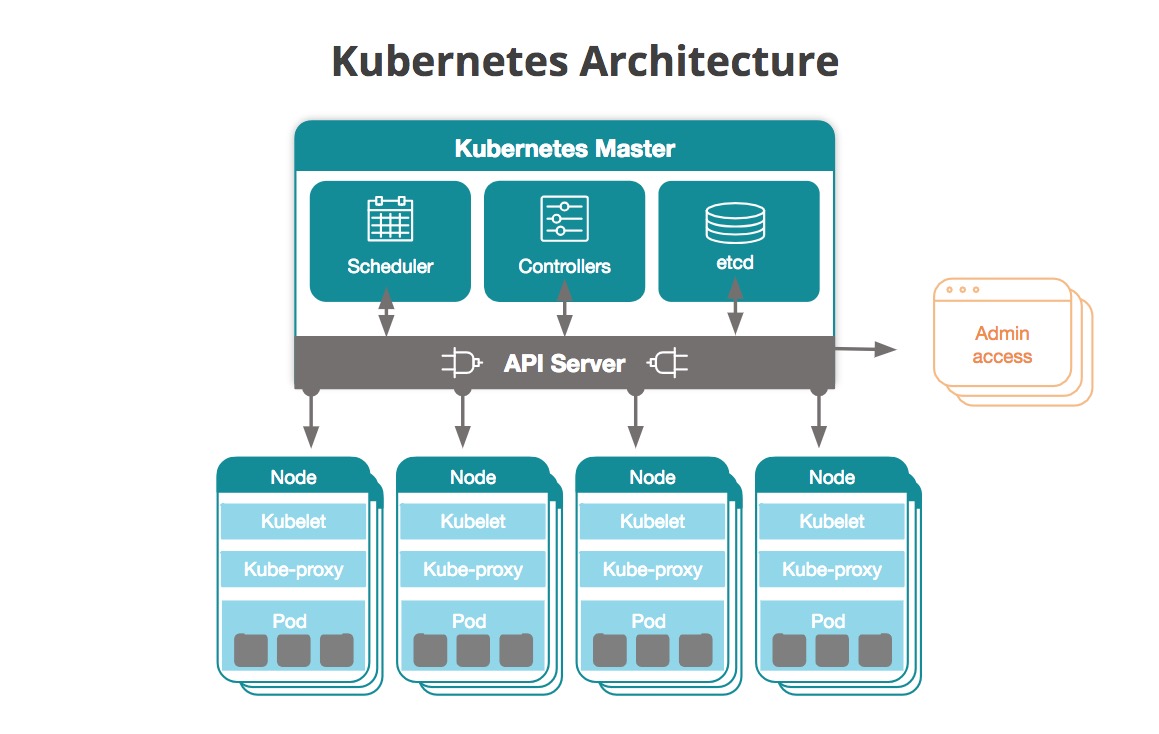
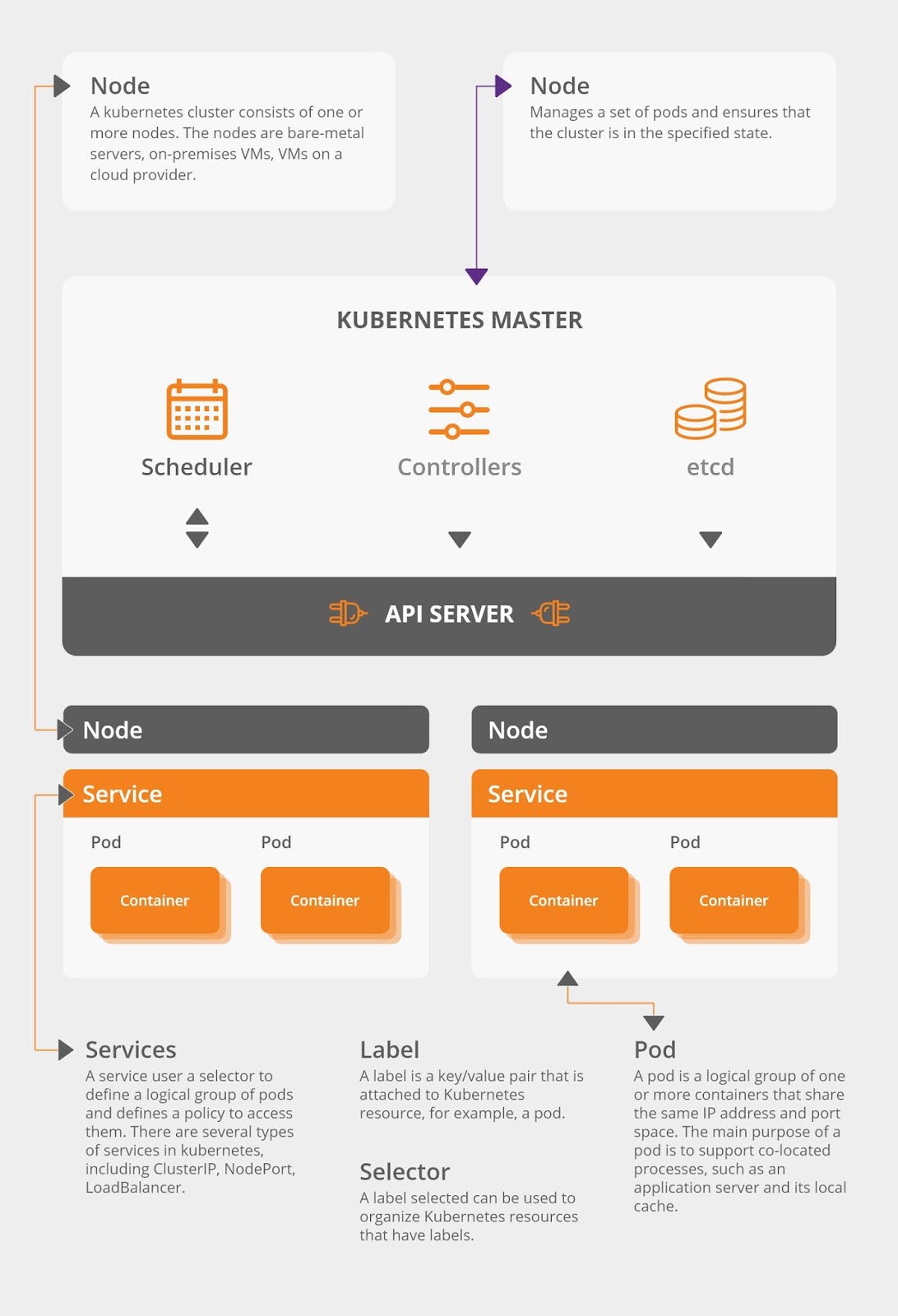
Kubernetes Architecture & High Availability
Understanding the architecture of Kubernetes is fundamental. This section covers the design principles, cluster setup guides for development, and automation techniques for production environments. Setting up a self-hosted cluster provides a strong foundation for learning how Kubernetes components interact.
Kubectl Tutorials
kubectl is the command-line tool used to interact with Kubernetes clusters. Learning how to use kubectl effectively is crucial for managing and troubleshooting your Kubernetes environment. This section includes tutorials on various commands and best practices for using kubectl.
Kubernetes Backup & Restore
Data integrity and availability are critical in any Kubernetes environment. This section explores tools like Velero for backing up and restoring Kubernetes clusters, ensuring that your data is protected against potential failures.
Kubernetes Native Resources
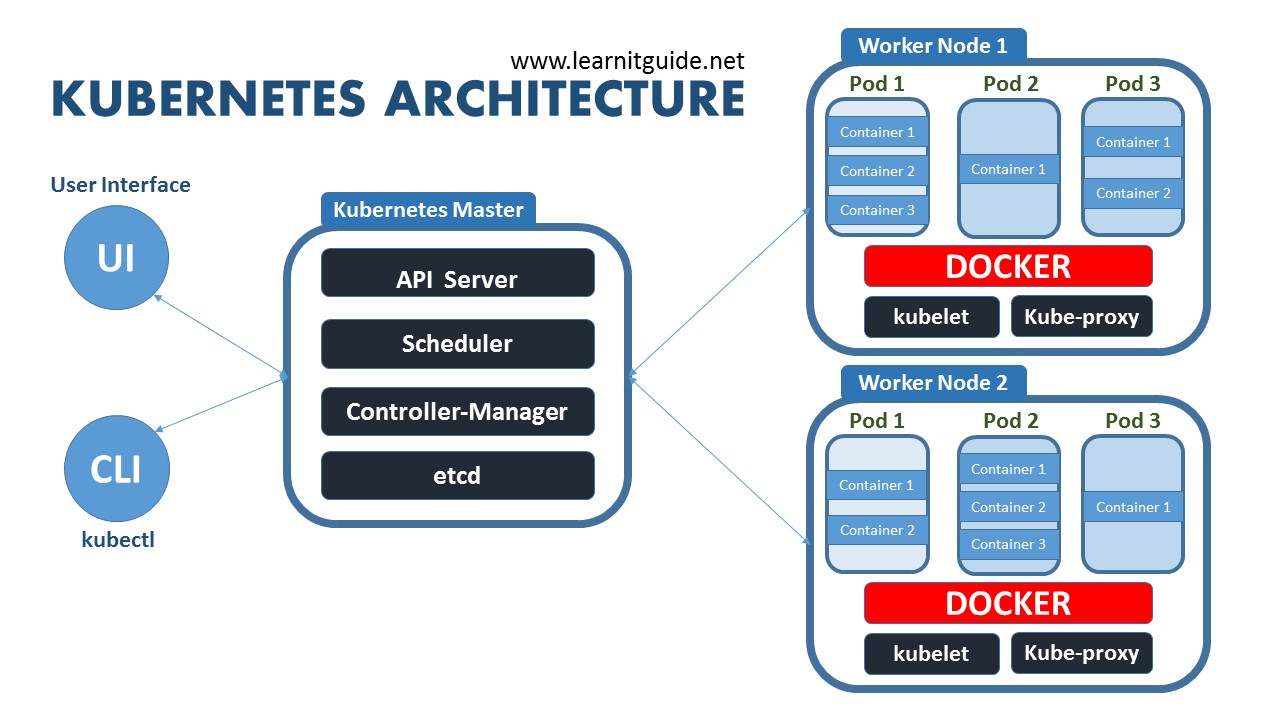
Kubernetes native resources such as deployments, pods, StatefulSets, and Jobs are essential for managing application lifecycle. This section provides tutorials on creating and managing these resources, helping you understand how to structure your applications effectively.
Kubernetes Monitoring & Logging
Monitoring and logging are vital for maintaining the health of your Kubernetes clusters. Tools like Prometheus and Grafana are commonly used for monitoring, while logging solutions ensure that you can track and analyze application behavior.
Troubleshooting Kubernetes
Even with the best configurations, issues can arise. This section covers common troubleshooting techniques for Kubernetes objects, including Pods, Deployments, and cluster components. Learning how to diagnose and resolve problems is essential for any Kubernetes user.
Advanced Kubernetes Concepts
As you progress, exploring advanced topics will deepen your understanding of Kubernetes. These include working with kubectl, load balancing, and real-world use cases.
Working with Kubectl
Mastering kubectl commands allows for efficient management of Kubernetes clusters. From deploying applications to inspecting cluster status, kubectl is an indispensable tool for any Kubernetes practitioner.
Load Balancing & Configurations
Kubernetes provides built-in load balancing capabilities to distribute traffic across containers effectively. Understanding how to configure load balancing ensures optimal performance and reliability for your applications.
Real-World Use Cases
Kubernetes is widely used in various industries, from web applications to big data processing. Exploring real-world use cases helps illustrate how Kubernetes can be applied to solve specific business challenges.
Conclusion
Kubernetes is a powerful platform that simplifies the management of containerized applications. Its features, such as automated deployment, scaling, and self-healing, make it an essential tool for modern DevOps practices. As more organizations adopt Kubernetes, the demand for skilled professionals continues to grow.
Whether you’re a beginner looking to start your journey or an experienced developer seeking to enhance your skills, there are numerous resources available to help you learn and master Kubernetes. From official documentation to online courses and community forums, the Kubernetes ecosystem offers a wealth of knowledge to support your learning path.
By understanding the core concepts and practical applications of Kubernetes, you can unlock new opportunities in the ever-evolving world of cloud-native technologies. Embrace the power of Kubernetes and take your career to new heights.








