
Understanding Financial Accounting: Key Concepts and Importance
Financial accounting is a critical component of the business world, providing a structured way for organizations to record, summarize, and report their financial activities. It serves as a foundation for decision-making, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder trust. Whether you’re an investor, a business owner, or a student exploring accounting careers, understanding financial accounting is essential. This article delves into the key concepts, principles, and importance of financial accounting in the United States.
What Is Financial Accounting?
Financial accounting refers to the process of recording, summarizing, and reporting a company’s financial transactions to external stakeholders such as investors, regulators, and creditors. The primary goal of financial accounting is to provide accurate and transparent financial information that reflects the organization’s financial health. This information is typically presented in the form of financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Key Components of Financial Accounting

- Financial Statements: These are the primary outputs of financial accounting. They include:
- Balance Sheet: Shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- Income Statement: Reports a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period.
-
Cash Flow Statement: Tracks the inflow and outflow of cash within a business.
-
GAAP Compliance: In the United States, financial accounting must adhere to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). These are a set of rules and standards that ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability in financial reporting.
-
Accounting Cycle: The process of recording and processing financial data involves several steps, including:
- Analyzing transactions
- Journalizing them
- Posting to ledgers
- Preparing trial balances
- Adjusting entries
- Preparing financial statements
- Closing entries
The 10 Principles of GAAP
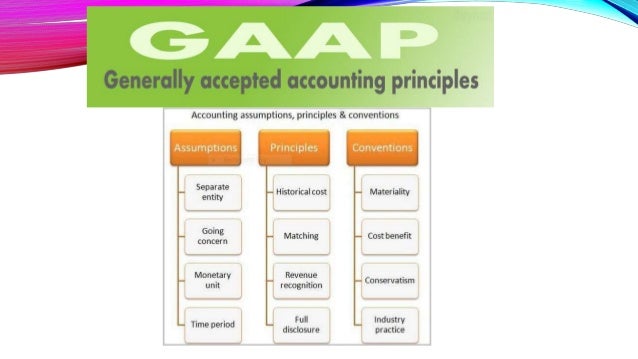
GAAP is built on ten core principles that guide financial accounting practices. These principles ensure that financial reports are reliable, consistent, and useful for decision-making. Here are some of the most important ones:
1. Principle of Regularity
This principle requires accountants to follow established GAAP rules consistently. For example, depreciation methods like the straight-line method must be applied uniformly each year.
2. Principle of Consistency
Once an accounting method is adopted, it should be used consistently across all reporting periods. This allows for meaningful comparisons of financial performance over time.
3. Principle of Sincerity
Financial reporting must be honest and based on factual evidence. Misrepresenting financial data violates this principle.
4. Principle of Non-Compensation
A company cannot offset its assets against liabilities or revenues against expenses. All aspects of financial performance must be reported separately.
5. Principle of Prudence
Accountants should exercise caution when reporting uncertain information. For example, potential losses should be recognized early, while gains should only be recorded when they are realized.
6. Principle of Continuity
This principle assumes that a business will continue operating for the foreseeable future. This allows for the use of historical cost accounting and depreciation.
7. Principle of Periodicity
Economic activities must be divided into specific time intervals, such as months or quarters, to enable regular financial reporting.
8. Principle of Materiality
Only information that could influence the decisions of financial statement users must be disclosed. Trivial matters can be disregarded.
9. Principle of Utmost Good Faith
All parties involved in the accounting process must act with honesty and integrity.
Financial Accounting vs. Managerial Accounting

While financial accounting focuses on external reporting, managerial accounting is concerned with internal decision-making. Here are the key differences:
Financial Accounting
- Focuses on external stakeholders
- Follows GAAP and IFRS standards
- Reports on past financial performance
- Produces financial statements for public disclosure
Managerial Accounting
- Focuses on internal management
- Not bound by strict accounting standards
- Uses forecasts and projections for strategic planning
- Provides detailed insights for operational decision-making
The Role of the FASB

The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is responsible for establishing and maintaining GAAP in the United States. As an independent organization, the FASB ensures that accounting standards remain relevant and effective. Its work is crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial reporting in the U.S.
Why Financial Accounting Matters
Financial accounting plays a vital role in the economy by ensuring transparency and accountability. Here are some reasons why it is important:
- Investor Confidence: Accurate financial reporting helps investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to GAAP and other standards ensures that businesses meet legal requirements.
- Creditworthiness: Lenders and creditors rely on financial statements to assess a company’s ability to repay loans.
- Operational Efficiency: Financial data provides insights into a company’s performance, helping managers identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Understanding financial accounting is essential for anyone involved in the business world. From preparing financial statements to adhering to GAAP, financial accounting ensures that organizations operate transparently and responsibly. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or an entrepreneur, mastering the principles of financial accounting can open doors to new opportunities and better decision-making. By staying informed and following best practices, you can contribute to a more stable and trustworthy financial ecosystem.








