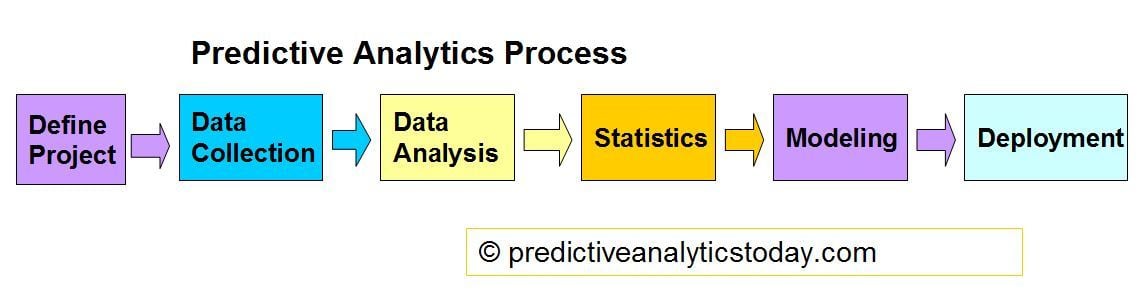
Understanding Predictive Analytics: A Comprehensive Guide
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool that leverages statistical techniques, machine learning, and data mining to analyze historical and current data in order to forecast future events. This approach enables businesses and organizations to make informed decisions by identifying patterns, relationships, and trends within large volumes of data. As the digital age continues to generate vast amounts of information, predictive analytics has become an essential component of strategic planning across various industries.
What Is Predictive Analytics?
At its core, predictive analytics involves the use of statistical models and algorithms to predict future outcomes based on past and present data. It is a forward-looking approach that differs from traditional business intelligence technologies, which are primarily focused on analyzing historical data for insights into past performance. Instead, predictive analytics uses this historical data to anticipate what might happen in the future, allowing organizations to proactively address potential risks and opportunities.
The process typically begins with data collection, where relevant information is gathered from various sources. This data is then processed and analyzed using advanced analytical techniques such as regression analysis, machine learning, and neural networks. These methods help uncover hidden patterns and correlations that can be used to make predictions about future events.
Key Techniques Used in Predictive Analytics

There are several key techniques employed in predictive analytics, each designed to extract valuable insights from data. These include:
1. Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical method used to determine the relationship between variables. It helps identify how changes in one variable affect another, making it useful for forecasting outcomes. For example, linear regression can be used to predict sales based on advertising spend, while logistic regression is often used for classification tasks, such as predicting whether a customer will churn.
2. Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables systems to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It involves training algorithms on historical data to recognize patterns and make predictions. Machine learning models can be supervised, unsupervised, or semi-supervised, depending on the type of data and the desired outcome.
3. Neural Networks
Neural networks are a type of machine learning model inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process information and learn from data. Neural networks are particularly effective at handling complex, non-linear relationships and are widely used in areas such as image recognition, natural language processing, and fraud detection.
4. Decision Trees
Decision trees are a simple yet powerful technique used to classify data and make predictions. They work by splitting data into branches based on specific criteria, creating a tree-like structure that represents different decision paths. Decision trees are easy to interpret and can be used for both classification and regression tasks.
5. Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is used to analyze data points collected over time. It helps identify trends, seasonality, and other patterns that can be used to forecast future values. Techniques such as ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) and exponential smoothing are commonly used in time series analysis.
Applications of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common use cases include:
1. Business and Marketing
In the business world, predictive analytics is used to optimize marketing strategies, improve customer retention, and enhance sales forecasting. By analyzing customer behavior and preferences, companies can create personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience.
2. Finance and Risk Management
Financial institutions use predictive analytics to assess credit risk, detect fraud, and manage investment portfolios. Credit scoring models, for instance, help lenders evaluate the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on a loan, enabling them to make more informed lending decisions.
3. Healthcare
In healthcare, predictive analytics is used to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency. Predictive models can help identify patients at high risk of developing certain conditions, allowing for early intervention and preventive care.
4. Supply Chain and Inventory Management

Predictive analytics plays a crucial role in supply chain management by helping businesses forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and reduce waste. By analyzing historical sales data and market trends, companies can make more accurate predictions about future demand, ensuring they have the right products in stock at the right time.
5. Human Resources
HR departments use predictive analytics to identify employee turnover risks, forecast workforce needs, and improve talent acquisition strategies. By analyzing employee performance data and other factors, organizations can develop targeted interventions to retain top talent and enhance productivity.
Benefits of Predictive Analytics
The benefits of predictive analytics are numerous and far-reaching. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing data-driven insights, predictive analytics helps organizations make more informed decisions.
- Cost Savings: Predictive models can help identify inefficiencies and reduce costs associated with waste, fraud, and poor resource allocation.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns can significantly improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Risk Mitigation: Predictive analytics enables businesses to anticipate and mitigate potential risks, such as credit defaults, supply chain disruptions, and cybersecurity threats.
Challenges and Limitations
While predictive analytics offers many benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. One of the main challenges is the quality and availability of data. Predictive models require large volumes of high-quality data to produce accurate results, and obtaining this data can be time-consuming and costly.
Another challenge is the complexity of the models themselves. Advanced techniques such as neural networks and deep learning require specialized knowledge and computational resources, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations. Additionally, there is always the risk of overfitting, where a model performs well on historical data but fails to generalize to new data.
The Future of Predictive Analytics
As technology continues to evolve, the future of predictive analytics looks promising. Advances in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and big data analytics are expected to further enhance the capabilities of predictive models. Additionally, the increasing availability of real-time data and the development of more user-friendly tools will make predictive analytics more accessible to a wider range of organizations.
In conclusion, predictive analytics is a powerful tool that can help organizations make informed decisions, reduce risks, and drive growth. By leveraging statistical techniques and advanced algorithms, businesses can gain valuable insights into future trends and outcomes, enabling them to stay ahead of the competition in an increasingly data-driven world.









